Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
| Brain: Tegmentum | ||
|---|---|---|
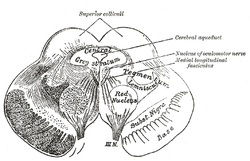
| Transverse section of mid-brain at level of superior colliculi. ("Tegmentum" visible center right.) | ||
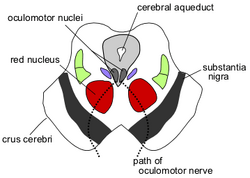
| Section through superior colliculus showing path of oculomotor nerve. (Tegmentum not labeled, but surrounding structures more clearly defined.) | ||
| Latin | Tegmentum | |
| Gray's | subject # | |
| Part of | ||
| Components | ||
| Artery | ||
| Vein | ||
| BrainInfo/UW | - | |
| MeSH | [1] | |
The tegmentum (from Latin for "covering") is a general area within the brainstem. It is located between the ventricular system and distinctive basal or ventral structures at each level. It is a multisynaptic network of neurons that is involved in many unconscious homeostatic and reflexive pathways.
Development[]
In embryos the tegmentum is the anterior half of the neural tube. However, for fetuses to adults, tegmentum only refers to the parts of the brain that remains relatively unchanged after development is complete, i.e. at the brain stem and midbrain. Other parts, on the other hand, develop further, through folding and thickening, and have different names. Still, it is considered a continuous central region through all levels of the brainstem.
Structures that develop to grow ventral or lateral outside this primitive tube as add-ons (e.g. the crus cerebri in the anterior of the midbrain) are not considered part of the 'tegmentum' as they are not part of the primitive neural tube but grow as projections from the cerebral cortex. Whereas, parts that were inside the primitive neural tube and remained an integral part of it after complete development (e.g. the red nucleus) are considered part of the tegmentum.
Divisions[]
The tegmentum forms distinguished divisions in the midbrain, pons and medulla
Midbrain tegmentum[]
- Main article: Midbrain tegmentum
The midbrain tegmentum is the part of the midbrain extending from the substantia nigra to the cerebral aqueduct in a horizontal section of the midbrain.
Pontine tegmentum[]
- Main article: pontine tegmentum
Lateral tegmental field[]
The lateral tegmental field (LTF) [1] is the source of several neurons of the noradrenaline system of the brain.
See also[]
Other pertinent areas of the tegmentum are:
- Ventral Tegmental area
- Periaqueductal Gray Matter
- Reticular Formation
- Red Nucleus
- Substantial Nigra
References[]
- Ackerman, T. F., Lamonte, N., & Bodnar, R. J. (2003). Lack of intersite GABA receptor subtype antagonist effects upon mu opioid receptor agonist-induced feeding elicited from either the ventral tegmental area or nucleus accumbens shell in rats: Physiology & Behavior Vol 79(2) Jul 2003, 191-198.
- Adell, A., & Artigas, F. (2004). The somatodendritic release of dopamine in the ventral tegmental area and its regulation by afferent transmitter systems: Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews Vol 28(4) Jul 2004, 415-431.
- Agars, K., & Kokkinidis, L. (1992). Scopolamine increases nonreinforced behavior in an intracranial self-stimulation discrimination paradigm: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 43(2) Oct 1992, 657-660.
- Ahmadi, S., Zarrindast, M. R., Nouri, M., Haeri-Rohani, A., & Rezayof, A. (2007). N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the ventral tegmental area are involved in retrieval of inhibitory avoidance memory by nicotine: Neurobiology of Learning and Memory Vol 88(3) Oct 2007, 352-358.
- Ainge, J. A., Keating, G. L., Latimer, M. P., & Winn, P. (2006). The Pedunculopontine Tegmental Nucleus and Responding for Sucrose Reward: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 120(3) Jun 2006, 563-570.
- Alderson, H. L., Jenkins, T. A., Kozak, R., Latimer, M. P., & Winn, P. (2001). The effects of excitotoxic lesions of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus on conditioned place preference to 4%, 12% and 20% sucrose solutions: Brain Research Bulletin Vol 56(6) Dec 2001, 599-605.
- Alderson, H. L., Latimer, M. P., & Winn, P. (2006). Intravenous self-administration of nicotine is altered by lesions of the posterior, but not anterior, pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 23(8) Apr 2006, 2169-2175.
- Almodovar-Fabregas, L. J., Segarra, O., Colon, N., Donnes, J. G., Mercado, M., Mejias-Aponte, C. A., et al. (2002). Effects of cocaine administration on VTA cell activity in response to prefrontal cortex stimulation. New York, NY: New York Academy of Sciences.
- Altier, N. (2000). An analysis of the role of midbrain dopamine systems in the suppression of tonic pain. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Altier, N., & Stewart, J. (1993). Intra-VTA infusions of the substance P analogue, DiMe-C7, and intra-accumbens infusions of amphetamine induce analgesia in the formalin test for tonic pain: Brain Research Vol 628(1-2) Nov 1993, 279-285.
- Altier, N., & Stewart, J. (1996). Opioid receptors in the ventral tegmental area contribute to stress-induced analgesia in the formalin test for tonic pain: Brain Research Vol 718(1-2) Apr 1996, 203-206.
- Altier, N., & Stewart, J. (1997). Neuropeptide FF in the VTA blocks the analgesic effects of both intra-VTA morphine and exposure to stress: Brain Research Vol 758(1-2) May 1997, 250-254.
- Altier, N., & Stewart, J. (1997). Tachykinin NK-1 and NK-3 selective agonists induce analgesia in the formalin test for tonic pain following intra-VTA or intra-accumbens microninfusions: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 89(1-2) Dec 1997, 151-165.
- Alvira-Botero, M. X., & Garzon, M. (2006). Cellular and subcellular distributions of delta opioid receptor activation sites in the ventral oral pontine tegmentum of the cat: Brain Research Vol 1123(1) Dec 2006, 101-111.
- Amici, R., Sanford, L. D., Kearney, K., McInerney, B., Ross, R. J., Horner, R. L., et al. (2004). A serotonergic (5-HT-sub-2) receptor mechanism in the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus participates in regulating the pattern of rapid-eye-movement sleep occurrence in the rat: Brain Research Vol 996(1) Jan 2004, 9-18.
- Andero, R., Torras-Garcia, M., Quiroz-Padilla, M. F., Costa-Miserachs, D., & Coll-Andreu, M. (2007). Electrical stimulation of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus in freely moving awake rats: Time- and site-specific effects on two-way active avoidance conditioning: Neurobiology of Learning and Memory Vol 87(4) May 2007, 510-521.
- Anderson, R., Diotte, M., & Miliaressis, E. (1995). The bidirectional interaction between ventral tegmental rewarding and hindbrain aversive stimulation effects in the rat: Brain Research Vol 688(1-2) Aug 1995, 15-20.
- Anzivino, L. A. (2007). Neurobehavioral functions of burst-firing in dopaminergic neurons. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Appel, S. B., Liu, Z., McElvain, M. A., & Brodie, M. S. (2003). Ethanol Excitation of Dopaminergic Ventral Tegmental Area Neurons Is Blocked by Quinidine: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 306(2) Aug 2003, 437-446.
- Arizzi-Lafrance, M. N. (2004). The effects of ethanol and ethanol metabolites on locomotor activity: Role of the substantia nigra pars reticulata. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Backes, E., & Hemby, S. E. (2003). Discrete Cell Gene Profiling of Ventral Tegmental Dopamine Neurons after Acute and Chronic Cocaine Self-Administration: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 307(2) Nov 2003, 450-459.
- Badiani, A., Leone, P., Noel, M. B., & Stewart, J. (1995). Ventral tegmental area opioid mechanisms and modulation of ingestive behavior: Brain Research Vol 670(2) Jan 1995, 264-276.
- Bahi, A., Boyer, F., Kafri, T., & Dreyer, J.-L. (2004). CD81-induced behavioural changes during chronic cocaine administration: in vivo gene delivery with regulatable lentivirus: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 19(6) Mar 2004, 1621-1633.
- Bailey, C. P., Manley, S. J., Watson, W. P., Wonnacott, S., Molleman, A., & Little, H. J. (1998). Chronic ethanol administration alters activity iin ventral tegmental area neurons after cessation of withdrawal hyperexcitability: Brain Research Vol 803(1-2) Aug 1998, 144-152.
- Balatoni, B., & Detari, L. (2003). EEG related neuronal activity in the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus of urethane anaesthetized rats: Brain Research Vol 959(2) Jan 2003, 304-311.
- Bals-Kubik, R., Ableitner, A., Herz, A., & Shippenberg, T. S. (1993). Neuroanatomical sites mediating the motivational effects of opioids as mapped by the conditioned place preference paradigm in rats: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 264(1) Jan 1993, 489-495.
- Bandyopadhya, R. S., Datta, S., & Saha, S. (2006). Activation of Pedunculopontine Tegmental Protein Kinase A: A Mechanism for Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Generation in the Freely Moving Rat: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 26(35) Aug 2006, 8931-8942.
- Bao, S., Chan, V. T., & Merzenich, M. M. (2001). Cortical remodelling induced by activity of ventral tegmental dopamine neurons: Nature Vol 412(6842) Jul 2001, 79-83.
- Barnea-Goraly, N., Menon, V., Eckert, M., Tamm, L., Bammer, R., Karchemskiy, A., et al. (2005). White matter development during childhood and adolescence: A crosssectional diffusion tensor imaging study: Cerebral Cortex Vol 15(12) Dec 2005, 1848-1854.
- Barr, G. A., & Rossi, G. (1992). Conditioned place preference from ventral tegmental injection of morphine in neonatal rats: Developmental Brain Research Vol 66(1) Mar 1992, 133-136.
- Bassant, M. H., & Poindessous-Jazat, F. (2002). Sleep-related increase in activity of mesopontine neurons in old rats: Neurobiology of Aging Vol 23(4) Jul-Aug 2002, 615-624.
- Bassett, J. P. (2006). The dorsal tegmental nucleus of gudden and angular velocity integration in the head direction system. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Bauco, P., Wang, Y., & Wise, R. A. (1993). Lack of sensitization or tolerance to the facilitating effect of ventral tegmental area morphine on lateral hypothalamic brain stimulation reward: Brain Research Vol 617(2) Jul 1993, 303-308.
- Bechara, A., & Van der Kooy, D. (1992). Chronic exposure to morphine does not alter the neural tissues subserving its acute rewarding properties: Apparent tolerance is overshadowing: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 106(2) Apr 1992, 364-373.
- Bechara, A., & Van der Kooy, D. (1992). A single brain stem substrate mediates the motivational effects of both opiates and food in nondeprived rats but not in deprived rats: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 106(2) Apr 1992, 351-363.
- Bechtholt, A. J., & Cunningham, C. L. (2005). Ethanol-Induced Conditioned Place Preference Is Expressed Through a Ventral Tegmental Area Dependent Mechanism: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 119(1) Feb 2005, 213-223.
- Bechtholt, A. J., Gremel, C. M., & Cunningham, C. L. (2004). Handling blocks expression of conditioned place aversion but not conditioned place preference produced by ethanol in mice: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 79(4) Dec 2004, 739-744.
- Beckstead, M. J., Ford, C. P., Phillips, P. E. M., & Williams, J. T. (2007). Presynaptic regulation of dendrodendritic dopamine transmission: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 26(6) Sep 2007, 1479-1488.
- Ben-Shahar, O., & Ettenberg, A. (1994). Repeated stimulation of the ventral tegmental area sensitizes the hyperlocomotor response to amphetamine: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 48(4) Aug 1994, 1005-1009.
- Berhow, M. T., Hiroi, N., Kobierski, L. A., Hyman, S. E., & et al. (1996). Influence of cocaine on the JAK-STAT pathway in the mesolimbic dopamine system: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 16(24) Dec 1996, 8019-8026.
- Bielajew, C., Bushnik, T., Konkle, A. T. M., & Schindler, D. (2000). The substrate for brain-stimulation reward in the lateral preoptic area II. Connections to the ventral tegmental area: Brain Research Vol 881(2) Oct 2000, 112-120.
- Bjijou, Y., Stinus, L., Moal, M. L., & Cador, M. (1996). Evidence for selective involvement of dopamine D-sub-1 receptors of the ventral tegmental area in the behavioral sensitization induced by intra-ventral tegmental area injections of D-amphetamine: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 277(2) May 1996, 1177-1187.
- Blaha, C. D., Allen, L. F., Das, S., Inglis, W. L., & et al. (1996). Modulation of dopamine efflux in the nucleus accumbens after cholinergic stimulation of the ventral tegmental area in intact, pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus-lesioned, and laterodorsal tegmental nucleus-lesioned rats: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 16(2) Jan 1996, 714-722.
- Bonci, A., & Malenka, R. C. (1999). Properties and plasticity of excitatory synapses on dopaminergic and GABAergic cells in the ventral tegmental area: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 19(10) May 1999, 3723-3730.
- Borgland, S. L., Malenka, R. C., & Bonci, A. (2004). Acute and Chronic Cocaine-Induced Potentiation of Synaptic Strength in the Ventral Tegmental Area: Electrophysiological and Behavioral Correlates in Individual Rats: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 24(34) Aug 2004, 7482-7490.
- Borowski, T. B., & Kokkinidis, L. (1992). Long-term influence of d-amphetamine on mesolimbic brain-stimulation reward: Comparison to chronic haloperidol and naloxone effects: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 43(1) Sep 1992, 1-15.
- Borowski, T. B., & Kokkinidis, L. (1996). Contribution of ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons to expression of conditional fear: Effects of electrical stimulation, excitotoxin lesions, and quinpirole infusion on potentiated startle in rats: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 110(6) Dec 1996, 1349-1364.
- Bossert, J. M., Liu, S. Y., Lu, L., & Shaham, Y. (2004). A Role of Ventral Tegmental Area Glutamate in Contextual Cue-Induced Relapse to Heroin Seeking: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 24(47) 2004, 10726-10730.
- Boye, S. M. (2005). Mesencephalic substrate of reward: Lesion effects: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 156(1) Jan 2005, 31-43.
- Boye, S. M., & Rompre, P.-P. (1996). Mesencephalic substrate of reward: Axonal connections: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 16(10) May 1996, 3511-3520.
- Brady, A. M., & O'Donnell, P. (2004). Dopaminergic Modulation of Prefrontal Cortical Input to Nucleus Accumbens Neurons In Vivo: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 24(5) Feb 2004, 1040-1049.
- Brebner, K., Phelan, R., & Roberts, D. C. S. (2000). Intra-VTA baclofen attenuates cocaine self-administration on a progressive ratio schedule of reinforcement: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 66(4) Aug 2000, 857-862.
- Bringmann, A. (1997). Nicotine affects the occipital theta rhythm after lesion of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus in rats: Neuropsychobiology Vol 35(2) Mar 1997, 102-107.
- Brioni, J. D., Kim, D. J. B., Brodie, M. S., Decker, M. W., & et al. (1995). ABT-418: Discriminative stimulus properties and effect on ventral tegmental cell activity: Psychopharmacology Vol 119(4) Jun 1995, 368-375.
- Broderick, P. A. (1992). Cocaine's colocalized effects on synaptic serotonin and dopamine in ventral tegmentum in a reinforcement paradigm: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 42(4) Aug 1992, 889-898.
- Brodie, M. S. (2002). Increased ethanol excitation of dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area after chronic ethanol treatment: Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research Vol 26(7) Jul 2002, 1024-1030.
- Brodie, M. S., & Appel, S. B. (1998). The effects of ethanol on dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area studied with intracellular recording in brain slices: Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research Vol 22(1) Feb 1998, 236-244.
- Brodie, M. S., & Bunney, E. B. (1996). Serotonin potentiates dopamine inhibition of ventral tegmental area neurons in vitro: Journal of Neurophysiology Vol 76(3) Sep 1996, 2077-2082.
- Brodie, M. S., McElvain, M. A., Bunney, E. B., & Appel, S. B. (1999). Pharmacological reduction of small conductance calcium-activated potassium current (SK) potentiates the excitatory effect of ethanol on ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 290(1) Jul 1999, 325-333.
- Brodie, M. S., Trifunovic, R. D., & Shefner, S. A. (1995). Serotonin potentiates ethanol-induced excitation of ventral tegmental area neurons in brain slices from three different rat strains: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 273(3) Jun 1995, 1139-1146.
- Brudzynski, S. M. (2001). Pharmacological and behavioral characteristics of 22 kHz alarm calls in rats: Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews Vol 25(7-8) Dec 2001, 611-617.
- Brudzynski, S. M., & Munoz, D. G. (1994). Chromogranin A applied to the nucleus accumbens decreases locomotor activity induced by activation of the mesolimbic dopaminergic system in the rat: Brain Research Bulletin Vol 35(3) 1994, 211-216.
- Bruijnzeel, A. W., & Markou, A. (2004). Adaptations in cholinergic transmission in the ventral tegmental area associated with the affective signs of nicotine withdrawal in rats: Neuropharmacology Vol 47(4) Sep 2004, 572-579.
- Bunney, E. B., Appel, S. B., & Brodie, M. S. (2001). Electrophysiological effects of cocaethylene, cocaine, and ethanol on dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 297(2) May 2001, 696-703.
- Bushnik Harris, T. L. (1994). Brain stimulation reward in the lateral preoptic area: An examination of its substrate and functional connectivity to the ventral tegmental area. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Byrnes, J. J., Pantke, M. M., Onton, J. A., & Hammer, R. P., Jr. (2000). Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase in the ventral tegmental area attenuates cocaine sensitization in rats: Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry Vol 24(2) Feb 2000, 261-273.
- Carey, R. J., Dai, H., Huston, J. P., Pinheiro-Carrera, M., & et al. (1995). L-DOPA metabolism in cortical and striatal tissues in an animal model of Parkinsonism: Brain Research Bulletin Vol 37(3) 1995, 295-299.
- Castro-Alamancos, M. A., & Borrell, J. (1992). Facilitation and recovery of shuttle box avoidance behavior after frontal cortex lesions is induced by a contingent electrical stimulation in the ventral tegmental nucleus: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 50(1-2) Sep 1992, 69-76.
- Centeno, S. (2002). Appetitive and consummatory sexual behaviors in the male rat following castration and testosterone replacement: The role of the ventral tegmental area. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Centonze, D., Usiello, A., Gubellini, P., Pisani, A., Borrelli, E., Bernardi, G., et al. (2002). Dopamine D2 receptor-mediated inhibition of dopaminergic neurons in mice lacking D2L receptors: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 27(5) Nov 2002, 723-726.
- Cervo, L., Rossi, C., Tatarczynska, E., & Samanin, R. (1992). Antidepressant-like effect of neurotensin administered in the ventral tegmental area in the forced swimming test: Psychopharmacology Vol 109(3) Nov 1992, 369-372.
- Champtiaux, N., Kalivas, P. W., & Bardo, M. T. (2006). Contribution of dihydro-beta-erythroidine sensitive nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the ventral tegmental area to cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in rats: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 168(1) Mar 2006, 120-126.
- Cheer, J. F., Kendall, D. A., Mason, R., & Marsden, C. A. (2003). Differential cannabinoid-induced electrophysiological effects in rat ventral tegmentum: Neuropharmacology Vol 44(5) Apr 2003, 633-641.
- Chen, J., Marmur, R., Pulles, A., Paredes, W., & et al. (1993). Ventral tegmental microinjection of !D-9-tetrahydrocannabinol enhances ventral tegmental somatodendritic dopamine levels but not forebrain dopamine levels: Evidence for local neural action by marijuana's psychoactive ingredient: Brain Research Vol 621(1) Sep 1993, 65-70.
- Chen, J., Nakamura, M., Kawamura, T., Takahashi, T., & Nakahara, D. (2006). Roles of pedunculopontine tegmental cholinergic receptors in brain stimulation reward in the rat: Psychopharmacology Vol 184(3-4) Mar 2006, 514-522.
- Chen, W. H., Tseng, Y. L., Lui, C. C., & Liu, J. S. (2005). Episodic pain syndrome restricted cheiro-oral region associated with pontine lesion: Brain Injury Vol 19(11) Oct 2005, 949-953.
- Chinto, A., Fulton, J., Koziel, N., Aziz, M., Sud, M., & Yeomans, J. S. (2003). Role of cholinergic receptors in locomotion induced by scopolamine and oxotremorine-M: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 76(1) Aug 2003, 53-61.
- Choi, K.-H., Clements, R. L. H., & Greenshaw, A. J. (2005). Simultaneous AMPA/kainate receptor blockade and dopamine D-sub(2/3) receptor stimulation in the nucleus accumbens decreases brain stimulation reward in rats: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 158(1) Mar 2005, 79-88.
- Choi, K.-H., Rahman, Z., Edwards, S., Hall, S., Neve, R. L., & Self, D. W. (2003). Opposite Effects of GluR1 and PKA-Resistant GluR1 Overexpression in the Ventral Tegmental Area on Cocaine Reinforcement. New York, NY: New York Academy of Sciences.
- Choulli, K., Herman, J. P., Abrous, N., & le Moal, M. (1987). Behavioral effects of intraaccumbens transplants in rats with lesions of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system: Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences Vol 495 Jun 1987, 497-508.
- Churchill, L., Klitenick, M. A., & Kalivas, P. W. (1998). Dopamine depletion reorganizes projections from the nucleus accumbens and ventral pallidum that mediate opioid-induced motor activity: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 18(19) Oct 1998, 8074-8085.
- Cincotta, M., Tozzi, F., Zaccara, G., Borgheresi, A., Lori, S., Cosottini, M., et al. (1999). Motor imagery in a locked-in patient: Evidence from transcranial magnetic stimulation: Italian Journal of Neurological Sciences Vol 20(1) Feb 1999, 37-41.
- Clark, A., & Little, H. J. (2004). Interactions between low concentrations of ethanol and nicotine on firing rate of ventral tegmental dopamine neurones: Drug and Alcohol Dependence Vol 75(2) Aug 2004, 199-206.
- Cline, E. J. (1991). Behavioral effects of intracerebral administration of the nicotine analogue cytisine in rats: Dissertation Abstracts International.
- Coco, M. L. (1997). Neural substrates for coping behavior in the rat: Possible importance of mesolimbocortical dopamine. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Coizet, V., Comoli, E., Westby, G. W. M., & Redgrave, P. (2003). Phasic activation of substantia nigra and the ventral tegmental area by chemical stimulation of the superior colliculus: An electrophysiological investigation in the rat: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 17(1) Jan 2003, 28-40.
- Colussi-Mas, J., Geisler, S., Zimmer, L., Zahm, D. S., & Berod, A. (2007). Activation of afferents to the ventral tegmental area in response to acute amphetamine: A double-labelling study: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 26(4) Aug 2007, 1011-1025.
- Cornish, J. L., & Kalivas, P. W. (2001). Repeated cocaine administration into the rat ventral tegmental area produces behavioral sensitization to a systemic cocaine challenge: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 126(1-2) Nov 2001, 205-209.
- Corrigall, W. A., Coen, K. M., & Adamson, K. L. (1994). Self-administered nicotine activates the mesolimbic dopamine system through the ventral tegmental area: Brain Research Vol 653(1-2) Aug 1994, 278-284.
- Corrigall, W. A., Coen, K. M., Adamson, K. L., & Chow, B. L. C. (1999). The mu opioid agonist DAMGO alters the intravenous self-administration of cocaine in rats: Mechanisms in the ventral tegmental area: Psychopharmacology Vol 141(4) Feb 1999, 428-435.
- Corrigall, W. A., Coen, K. M., Adamson, K. L., Chow, B. L. C., & Zhang, J. (2000). Response of nicotine self-administration in the rat to manipulations of mu-opioid and gamma -aminobutyric acid receptors in the ventral tegmental area: Psychopharmacology Vol 149(2) Apr 2000, 107-114.
- Corrigall, W. A., Coen, K. M., Zhang, J., & Adamson, K. L. (2001). GABA mechanisms in the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus influence particular aspects of nicotine self-administration selectively in the rat: Psychopharmacology Vol 158(2) Nov 2001, 190-197.
- Corrigall, W. A., Coen, K. M., Zhang, J., & Adamson, K. L. (2002). Pharmacological manipulations of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus in the rat reduce self-administration of both nicotine and cocaine: Psychopharmacology Vol 160(2) Mar 2002, 198-205.
- Covington, H. E. (2006). Intense cocaine taking and social stress: Role of NMDA receptors in the ventral tegmental area. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Crawley, J. N. (1992). Subtype-selective cholecystokinin receptor antagonists block cholecystokinin modulation of dopamine-mediated behaviors in the rat mesolimbic pathway: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 12(9) Sep 1992, 3380-3391.
- Crescimanno, G., Sorbera, F., Emmi, A., & Amato, G. (1998). Inhibitory effect of A10 dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area on the orienting response evoked by acoustic stimulation in the cat: Brain Research Bulletin Vol 45(1) 1998, 61-65.
- Crochet, S., & Sakai, K. (2003). Dopaminergic Modulation of Behavioral States in Mesopontine Tegmentum: A Reverse Microdialysis Study in Freely Moving Cats: Sleep: Journal of Sleep and Sleep Disorders Research Vol 26(7) Nov 2003, 801-806.
- Curtis, J. T., & Wang, Z. (2005). Ventral tegmental area involvement in pair bonding in male prairie voles: Physiology & Behavior Vol 86(3) Oct 2005, 338-346.
- Dahan, L., Astier, B., Vautrelle, N., Urbain, N., Kocsis, B., & Chouvet, G. (2007). Prominent burst firing of dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area during paradoxical sleep: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 32(6) Jun 2007, 1232-1241.
- Dalia, A., Uretsky, N. J., & Wallace, L. J. (1996). Induction of locomotor activity by the glutamate antagonist DNQX injected into the ventral tegmental area: Brain Research Vol 728(2) Jul 1996, 209-214.
- Datta, S., Mavanji, V., Patterson, E. H., & Ulloor, J. (2003). Regulation of Rapid Eye Movement Sleep in the Freely Moving Rat: Local Microinjection of Serotonin, Norepinephrine, and Adenosine into the Brainstem: Sleep: Journal of Sleep and Sleep Disorders Research Vol 26(5) Aug 2003, 513-520.
- Dauge, V., Kalivas, P. W., Duffy, T., & Roques, B. P. (1992). Effect of inhibiting enkephalin catabolism in the VTA on motor activity and extracellular dopamine: Brain Research Vol 599(2) Dec 1992, 209-214.
- David, V., & Cazala, P. (1994). A comparative study of self-administration of morphine into the amygdala and the ventral tegmental area in mice: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 65(2) Dec 1994, 205-211.
- David, V., & Cazala, P. (1996). Preference for self-administration of a low dose of morphine into the ventral tegmental area rather than into the amygdala in mice: Psychobiology Vol 24(3) Sep 1996, 211-218.
- David, V., Durkin, T. P., & Cazala, P. (1997). Self-administration of the GABA-sub(A ) antagonist bicuculline into the ventral tegmental area in mice: Dependence on D-sub-2 dopaminergic mechanisms: Psychopharmacology Vol 130(2) Mar 1997, 85-90.
- David, V., Durkin, T. P., & Cazala, P. (2002). Differential effects of the dopamine D-sub-2/D-sub-3 receptor antagonist sulpiride on self-administration of morphine into the ventral tegmental area or the nucleus accumbens: Psychopharmacology Vol 160(3) Mar 2002, 307-317.
- David, V., Segu, L., Buhot, M.-C., Ichaye, M., & Cazala, P. (2004). Rewarding effects elicited by cocaine microinjections into the ventral tegmental area of C57BL/6 mice: Involvement of dopamine D-sub-1 and serotonin-sub(1B) receptors: Psychopharmacology Vol 174(3) Jul 2004, 367-375.
- De La Garza Ii, R., Callahan, P. M., & Cunningham, K. A. (1998). The discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine: Effects of microinfusion of cocaine, a 5-HT-sub(1A ) agonist or antagonist, into the ventral tegmental area: Psychopharmacology Vol 137(1) May 1998, 1-6.
- DeBold, J. F., & Frye, C. A. (1994). Genomic and non-genomic actions of progesterone in the control of female hamster sexual behavior: Hormones and Behavior Vol 28(4) Dec 1994, 445-453.
- DeBold, J. F., & Frye, C. A. (1994). Progesterone and the neural mechanisms of hamster sexual behavior: Psychoneuroendocrinology Vol 19(5-7) 1994, 563-579.
- Depue, R. A., & Collins, P. F. (1999). Neurobiology of the structure of personality: Dopamine, facilitation of incentive motivation, and extraversion: Behavioral and Brain Sciences Vol 22(3) Jun 1999, 491-569.
- Deurveilher, S., Delamanche, I. S., Hars, B., Breton, P., & Hennevin, E. (1999). Chronic, low-level exposure to the cholinesterase inhibitor DFP. I: Time course of neurochemical changes in the rat pontomesencephalic tegmentum: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 64(1) Sep 1999, 95-103.
- Devine, D. P. (1994). The involvement of ventral tegmental opioid receptors in mediation of opiate-reward and in modulation of mesolimbic dopamine: Behavioural and neurochemical analyses. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Di Ciano, P., & Everitt, B. J. (2004). Contribution of the ventral tegmental area to cocaine-seeking maintained by a drug-paired conditioned stimulus in rats: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 19(6) Mar 2004, 1661-1667.
- Di Matteo, V., & Esposito, E. (2003). Serotonin Control of Dopaminergic Neurotransmission: Focus on 5-HT-sub-2 Receptors: Current Neuropharmacology Vol 1(2) Jun 2003, 153-164.
- Diana, M., Gessa, G. L., & Rossetti, Z. L. (1992). Lack of tolerance to ethanol-induced stimulation of mesolimbic dopamine system: Alcohol and Alcoholism Vol 27(4) Jul 1992, 329-333.
- Diaz-Mataix, L., Artigas, F., & Celada, P. (2006). Activation of pyramidal cells in rat medial prefrontal cortex projecting to ventral tegmental area by a 5-HT-sub(1A) receptor agonist: European Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 16(4) May 2006, 288-296.
- Diederich, K., & Koch, M. (2005). Role of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus in sensorimotor gating and reward-related behavior in rats: Psychopharmacology Vol 179(2) May 2005, 402-408.
- Diotte, M., Bielajew, C., Miguelez, M., & Miliaressis, E. (2001). Factors that influence the persistence of stimulation-induced aversion: Physiology & Behavior Vol 72(5) Apr 2001, 661-667.
- Djouma, E., & Lawrence, A. J. (2002). The Effect of Chronic Ethanol Consumption and Withdrawal on mu -Opioid and Dopamine D-sub-1 and D-sub-2 Receptor Density in Fawn-Hooded Rat Brain: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 302(2) Aug 2002, 551-559.
- Doherty, M., & Gratton, A. (2007). Differential involvement of ventral tegmental GABA-sub(A) and GABA-sub(B) receptors in the regulation of the nucleus accumbens dopamine response to stress: Brain Research Vol 1150 May 2007, 62-68.
- Dohrman, D. P., & Reiter, C. K. (2003). Chronic ethanol reduces nicotine-induced dopamine release in PC12 cells: Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research Vol 27(11) Nov 2003, 1846-1851.
- Dremencov, E., Nahshoni, E., Levy, D., Mintz, M., Overstreet, D. H., Weizman, A., et al. (2004). Dimensional complexity of the neuronal activity in a rat model of depression: Neuroreport: For Rapid Communication of Neuroscience Research Vol 15(12) Aug 2004, 1983-1986.
- Driagin, Y. M. (1994). Analysis of the caudate-ventrotegmental effects on alimentary conditioning in cats: Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal SSSR im I M Sechenova Vol 80(1) Jan 1994, 142-145.
- Driagin, Y. M. (1995). The effect of orbital cortex on the unit activity of the midbrain tegmentum in food conditioning in cats: Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal SSSR im I M Sechenova Vol 81(4) Apr 1995, 76-82.
- Druhan, J. P. (1990). An assessment of the effects of psychoactive drugs and electrical stimulation of the ventral tegmental area on the stimulus properties of amphetamine: Dissertation Abstracts International.
- Druhan, J. P., Deschamps, S.-E., & Stewart, J. (1993). D-amphetamine-like stimulus properties are produced by morphine injections into the ventral tegmental area but not into the nucleus accumbens: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 59(1-2) Dec 1993, 41-51.
- Dryagin, Y. M. (1995). Analysis of the caudatoventrotegmental influences during the realization of the motor alimentary conditioned reflexes: Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology Vol 25(2) Mar-Apr 1995, 130-132.
- Dryagin, Y. M. (1997). Effect of the orbital cortex on the neuronal activity of the tegmentum of the midbrain during a feeding reflex in cats: Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology Vol 27(1) Jan-Feb 1997, 87-91.
- Due, D. L. (2001). A study of the physiologic and cognitive contributions of mesocorticolimbic dopamine circuits to stimulus salience detection in smokers. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Dunbar, J. S., Hitchcock, K., Latimer, M., Rugg, E. L., & et al. (1992). Excitotoxic lesions of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus of the rat: II. Examination of eating and drinking, rotation, and reaching and grasping following unilateral ibotenate or quinolinate lesions: Brain Research Vol 589(2) Sep 1992, 194-206.
- Duncan, C. C., & Fernando, P. W. (1991). Effects of tetrahydropapaveroline in the nucleus accumbens and the ventral tegmental area on ethanol preference in the rat: Alcohol Vol 8(2) Mar-Apr 1991, 87-90.
- Dunn, J. M., Inderwies, B. R., Licata, S. C., & Pierce, R. C. (2005). Repeated administration of AMPA or a metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist into the rat ventral tegmental area augments the subsequent behavioral hyperactivity induced by cocaine: Psychopharmacology Vol 179(1) Apr 2005, 172-180.
- Echo, J. A. (2002). The role of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters upon opioid-induced feeding in the nucleus accumbens shell and ventral tegmental area in rats. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Echo, J. A., Lamonte, N., Ackerman, T. F., & Bodnar, R. J. (2002). Alterations in food intake elicited by GABA and opioid agonists and antagonists administered into the ventral tegmental area region of rats: Physiology & Behavior Vol 76(1) May 2002, 107-116.
- Eiler, W. J. A., II, & June, H. L. (2007). Blockade of GABA-sub(A) receptors within the extended amygdala attenuates D-sub-2 regulation of alcohol-motivated behaviors in the ventral tegmental area of alcohol-preferring (P) rats: Neuropharmacology Vol 52(8) Jun 2007, 1570-1579.
- Elliott, P. J., Paris, J. M., Mitsushio, H., & Lorens, S. A. (1990). Neuronal sites mediating locomotor hyperactivity following central neurokinin agonist administration: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 37(2) Oct 1990, 329-333.
- Enrico, P., Bouma, M., de Vries, J. B., & Westerink, B. H. C. (1998). The role of afferents to the ventral tegmental area in the handling stress-induced increase in the release of dopamine in the medial prefrontal cortex: A dual-probe microdialysis study in the rat brain: Brain Research Vol 779(1-2) Jan 1998, 205-213.
- Fagen, Z. M., Mansvelder, H. D., Keath, J. R., & McGehee, D. S. (2003). Short- and Long-Term Modulation of Synaptic Inputs to Brain Reward Areas by Nicotine. New York, NY: New York Academy of Sciences.
- Fairhurst, M., Wiech, K., Dunckley, P., & Tracey, I. (2007). Anticipatory brainstem activity predicts neural processing of pain in humans: Pain Vol 128(1-2) Mar 2007, 101-110.
- Faleiro, L. J., Jones, S., & Kauer, J. A. (2003). Rapid AMPAR/NMDAR Response to Amphetamine: A Detectable Increase in AMPAR/NMDAR Ratios in the Ventral Tegmental Area Is Detectable after Amphetamine Injection. New York, NY: New York Academy of Sciences.
- Faleiro, L. J., Jones, S., & Kauer, J. A. (2004). Rapid Synaptic Plasticity of Glutamatergic Synapses on Dopamine Neurons in the Ventral Tegmental Area in Response to Acute Amphetamine Injection: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 29(12) Dec 2004, 2115-2125.
- Feenstra, M. G., Kalsbeek, A., & Van Galen, H. (1992). Neonatal lesions of the ventral tegmental area affect monoaminergic responses to stress in the medial prefrontal cortex and other dopamine projection areas in adulthood: Brain Research Vol 596(1-2) Nov 1992, 169-182.
- Feifel, D., & Reza, T. L. (1999). Effects of neurotensin administered into the ventral tegmental area on prepulse inhibition of startle: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 106(1-2) Dec 1999, 189-193.
- Fenzl, T., & Schuller, G. (2002). Periaqueductal gray and the region of the paralemniscal area have different functions in the control of vocalization in the neotropical bat, Phyllostomus discolor: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 16(10) Nov 2002, 1974-1986.
- Ferraz, A. C., Xavier, L. L., Hernandes, S., Sulzbach, M., Viola, G. G., Anselmo-Franci, J. A., et al. (2003). Failure of estrogen to protect the substantia nigra pars compacta of female rats from lesion induced by 6-hydroxydopamine: Brain Research Vol 986(1-2) Oct 2003, 200-205.
- Fields, H. L., Hjelmstad, G. O., Margolis, E. B., & Nicola, S. M. (2007). Ventral tegmental area neurons in learned appetitive behavior and positive reinforcement: Annual Review of Neuroscience Vol 30 2007, 289-316.
- Figlewicz, D. P., Evans, S. B., Murphy, J., Hoen, M., & Baskin, D. G. (2003). Expression of receptors for insulin and leptin in the ventral tegmental area/substantia nigra (VTA/SN) of the rat: Brain Research Vol 964(1) Feb 2003, 107-115.
- Finn, P. D., & Yahr, P. (1994). Projection of the sexually dimorphic area of the gerbil hypothalamus to the retrorubral field is essential for male sexual behavior: Role of A8 and other cells: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 108(2) Apr 1994, 362-378.
- Fiorillo, C. D., & Williams, J. T. (1998). Glutamate mediates an inhibitory postsynaptic potential in dopamine neurons: Nature Vol 394(6688) Jul 1998, 78-82.
- Fiorino, D. F., Coury, A., Fibiger, H. C., & Phillips, A. G. (1993). Electrical stimulation of reward sites in the ventral tegmental area increases dopamine transmission in the nucleus accumbens of the rat: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 55(2), Spec Issue Jun 1993, 131-141.
- Fletcher, P. J., Chintoh, A. F., Sinyard, J., & Higgins, G. A. (2004). Injection of the 5-HT-sub(2C ) Receptor Agonist Ro60-0175 into the Ventral Tegmental Area Reduces Cocaine-Induced Locomotor Activity and Cocaine Self-Administration: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 29(2) Feb 2004, 308-318.
- Floody, O. R., & DeBold, J. F. (2004). Effects of midbrain lesions on lordosis and ultrasound production: Physiology & Behavior Vol 82(5) Oct 2004, 791-804.
- Flores, C., Arvanitogiannis, A., & Shizgal, P. (1997). Fos-like immunoreactivity in forebrain regions following self-stimulation of the lateral hypothalamus and the ventral tegmental area: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 87(2) Sep 1997, 239-251.
- Flores, C., Stewart, J., Salmaso, N., Zhang, Y., & Boksa, P. (2002). Astrocytic basic fibroblast growth factor expression in dopaminergic regions after perinatal anoxia: Biological Psychiatry Vol 52(4) Aug 2002, 362-370.
- Floresco, S. B. (2000). Limbic-striatal interactions and their modulation by dopamine: Electrophysiological, neurochemical and behavioral analyses. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Floresco, S. B., Todd, C. L., & Grace, A. A. (2001). Glutamatergic afferents from the hippocampus to the nucleus accumbens regulate activity of ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 21(13) Jul 2001, 4915-4922.
- Florio, T., Capozzo, A., Puglielli, E., Pizzuti, G., & Scarnati, E. (1999). The function of the pedunculopontine nucleus in the preparation and execution of an externally-cued bar pressing task in the rat: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 104(1-2) Oct 1999, 95-104.
- Foddai, M., Dosia, G., Spiga, S., & Diana, M. (2004). Acetaldehyde increases dopaminergic neuronal activity in the VTA: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 29(3) Mar 2004, 530-536.
- Forster, G. L., & Blaha, C. D. (2000). Laterodorsal tegmental stimulation elicits dopamine efflux in the rat nucleus accumbens by activation of acetylcholine and glutamate receptors in the ventral tegmental area: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 12(10) Oct 2000, 3596-3604.
- Forster, G. L., & Blaha, C. D. (2003). Pedunculopontine tegmental stimulation evokes striatal dopamine efflux by activation of acetylcholine and glutamate receptors in the midbrain and pons of the rat: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 17(4) Feb 2003, 751-762.
- Franchi e Vasconcelos, C. R., & Hoffman, A. (1994). Involvement of the cholinergic system and the basal midbrain in the organization of tonic immobility in the toad Bufo paracnemis: Physiology & Behavior Vol 55(5) May 1994, 831-837.
- Frankle, W. G., Laruelle, M., & Haber, S. N. (2006). Prefrontal Cortical Projections to the Midbrain in Primates: Evidence for a Sparse Connection: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 31(8) Aug 2006, 1627-1636.
- French, E. D. (1994). Phencyclidine and the midbrain dopamine system: Electrophysiology and behavior: Neurotoxicology and Teratology Vol 16(4) Jul-Aug 1994, 355-362.
- Frohardt, R. J., Bassett, J. P., & Taube, J. S. (2006). Path Integration and Lesions Within the Head Direction Cell Circuit: Comparison Between the Roles of the Anterodorsal Thalamus and Dorsal Tegmental Nucleus: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 120(1) Feb 2006, 135-149.
- Frye, C. A. (1993). Progestins' non-genomic actions within the ventral tegmental area are essential for sexual receptivity in female hamsters: Dissertation Abstracts International.
- Frye, C. A., & DeBold, J. F. (1993). P-3-BSA, but not P-11-BSA, implants in the VTA rapidly facilitate receptivity in hamsters after progesterone priming to the VMH: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 53(1-2) Feb 1993, 167-175.
- Frye, C. A., & Leadbetter, E. A. (1994). 5!a-Reduced progesterone metabolites are essential in hamster VTA for sexual receptivity: Life Sciences Vol 54(10) 1994, 653-659.
- Frye, C. A., Mermelstein, P. G., & DeBold, J. F. (1992). Evidence for a non-genomic action of progestins on sexual receptivity in hamster ventral tegmental area but not hypothalamus: Brain Research Vol 578(1-2) Apr 1992, 87-93.
- Frye, C. A., Mermelstein, P. G., & DeBold, J. F. (1993). Bicuculline infused into the hamster ventral tegmentum inhibits, while sodium valproate facilitates, sexual receptivity: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 46(1) Sep 1993, 1-8.
- Frye, C. A., & Petralia, S. M. (2003). Mitochondrial Benzodiazepine Receptors in the Ventral Tegmental Area Modulate Sexual Behaviour of Cycling or Hormone-Primed Hamsters: Journal of Neuroendocrinology Vol 15(7) Jul 2003, 677-686.
- Frye, C. A., & Petralia, S. M. (2004). 3alpha ,5alpha -THP's Actions in the Ventral Tegmental Area for Lordosis: A Model System for Defining Mechanisms and Function of Progestins. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
- Frye, C. A., & Rhodes, M. E. (2008). Infusions of 3alpha ,5alpha -THP to the VTA enhance exploratory, anti-anxiety, social, and sexual behavior and increase levels of 3alpha ,5alpha -THP in middbrain, hippocampus, diencephalon, and cortex of female rats: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 187(1) Feb 2008, 88-99.
- Frye, C. A., & Vongher, J. M. (1999). GABA-sub(A), D-sub-1, and D-sub-5, but not progestin receptor, antagonist and anti-sense oligonucleotide infusions to the ventral tegmental area of cycling rats and hamsters attenuate lordosis: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 103(1) Aug 1999, 23-34.
- Frye, C. A., & Vongher, J. M. (1999). Progestins' Rapid Facilitation of Lordosis When Applied to the Ventral Tegmentum Corresponds to Efficacy at Enhancing GABA-sub(A) Receptor Activity: Journal of Neuroendocrinology Vol 11(11) Nov 1999, 829-837.
- Frye, C. A., & Vongher, J. M. (2001). Ventral tegmental area infusions of inhibitors of the biosynthesis and metabolism of 3alpha ,5alpha -THP attenuate lordosis of hormone-primed and behavioural oestrous rats and hamsters: Journal of Neuroendocrinology Vol 13(12) Dec 2001, 1076-1086.
- Frye, C. A., & Walf, A. A. (2007). In the ventral tegmental area, the membrane-mediated actions of progestins for lordosis of hormone-primed hamsters involve phospholipase C and protein kinase C: Journal of Neuroendocrinology Vol 19(9) Sep 2007, 717-724.
- Frye, C. A., Walf, A. A., & Petralia, S. M. (2006). In the ventral tegmental area, progestins have actions at D-sub-1 receptors for lordosis of hamsters and rats that involve GABA-sub(A) receptors: Hormones and Behavior Vol 50(2) Aug 2006, 332-337.
- Frye, C. A., Walf, A. A., & Petralia, S. M. (2006). Progestin facilitation of lordosis in rodents involves adenylyl cyclase activity in the ventral tegmental area: Hormones and Behavior Vol 50(2) Aug 2006, 237-244.
- Frye, C. A., Walf, A. A., & Petralia, S. M. (2006). Progestins' effects on sexual behaviour of female rats and hamsters involving D-sub-1 and GABA-sub(A) receptors in the ventral tegmental area may be G-protein-dependent: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 172(2) Jul 2006, 286-293.
- Frye, C. A., Walf, A. A., & Sumida, K. (2004). Progestins' actions in the VTA to facilitate lordosis involve dopamine-like type 1 and 2 receptors: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 78(3) Jul 2004, 405-418.
- Gallagher, S. P. (2003). Functional interrelationships between the optic tectum and nucleus isthmi in two teleost fishes. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Gallant, D. M., & Head-Dunham, R. (1991). Tetrahydropapaveroline and alcohol preference: Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research Vol 15(5) Oct 1991, 900.
- Gallegos, R. A., Lee, R.-S., Criado, J. R., Henriksen, S. J., & Steffensen, S. C. (1999). Adaptive response of psi -aminobutyric acid neurons in the ventral tegmental area of chronic ethanol: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 291(3) Dec 1999, 1045-1053.
- Gatto, G. J. (1993). Reward-relevant actions of alcohol in selectively bred lines of rats: Dissertation Abstracts International.
- Gatto, G. J., McBride, W. J., Murphy, J. M., Lumeng, L., & et al. (1994). Ethanol self-infusion into the ventral tegmental area by alcohol-preferring rats: Alcohol Vol 11(6) Nov-Dec 1994, 557-564.
- Georges, F., & Aston-Jones, G. (2001). Potent regulation of midbrain dopamine neurons by the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 21(16) Aug 2001, RC160.
- Georges, F., & Aston-Jones, G. (2003). Prolonged activation of mesolimbic dopaminergic neurons by morphine withdrawal following clonidine: Participation of imidazoline and norepinephrine receptors: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 28(6) 2003, 1140-1149.
- Georges, F., Le Moine, C., & Aston-Jones, G. (2006). No Effect of Morphine on Ventral Tegmental Dopamine Neurons during Withdrawal: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 26(21) May 2006, 5720-5726.
- Gifkins, A., Greba, Q., & Kokkinidis, L. (2002). Ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons mediate the shock sensitization of acoustic startle: A potential site of action for benzodiazepine anxiolytics: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 116(5) Oct 2002, 785-794.
- Giordano, M., Guemes, M., Lopez-Arias, V., & Paredes, R. G. (1998). Socio-sexual behavior in male rats after lesions of the dorsolateral tegmentum: Physiology & Behavior Vol 65(1) Aug 1998, 89-94.
- Giorgetti, M., Hotsenpiller, G., Ward, P., Teppen, T., & Wolf, M. E. (2001). Amphetamine-induced plasticity of AMPA receptors in the ventral tegmental area: Effects on extracellular levels of dopamine and glutamate in freely moving rats: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 21(16) Aug 2001, 6362-6369.
- Glenthoj, B., Mogensen, J., Laursen, H., Holm, S., & et al. (1993). Electrical sensitization of the meso-limbic dopaminergic system in rats: A pathogenetic model for schizophrenia: Brain Research Vol 619(1-2) Aug 1993, 39-54.
- Gobbi, G., Muntoni, A. L., Gessa, G. L., & Diana, M. (2001). Clonidine fails to modify dopaminergic neuronal activity during morphine withdrawal: Psychopharmacology Vol 158(1) Oct 2001, 1-6.
- Goloshchapov, A. V., Filipenko, M. L., Bondar, N. P., Kudryavtseva, N. N., & Van Ree, J. M. (2005). Decrease of kappa -opioid receptor mRNA level in ventral tegmental area of male mice after repeated experience of aggression: Molecular Brain Research Vol 135(1-2) Apr 2005, 290-292.
- Gong, W., Justice, J. B., Jr., & Neill, D. (1997). Dissociation of locomotor and conditioned place preference responses following manipulation of GABA-A and AMPA receptors in ventral pallidum: Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry Vol 21(5) Jul 1997, 839-852.
- Gong, W., Neill, D., & Justice, J. B. (1996). Conditioned place preference and locomotor activation produced by injection of psychostimulants into ventral pallidum: Brain Research Vol 707(1) Jan 1996, 64-74.
- Gorbachevskaya, A. I. (1998). Projections of the amygdaloid body, ventral tegmental area, and substantia nigra to various segments of the nucleus accumbens in the dog brain: Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology Vol 28(6) Nov-Dec 1998, 715-719.
- Gorbachevskaya, A. I. (2000). Projections of the substantial nigra, ventral tegmental area, and amygdaloid body to the pallidum in the dog brain: Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology Vol 30(1) Jan-Feb 2000, 107-110.
- Goto, Y., & O'Donnell, P. (2004). Prefrontal Lesion Reverses Abnormal Mesoaccumbens Response in an Animal Model of Schizophrenia: Biological Psychiatry Vol 55(2) Jan 2004, 172-176.
- Grant, S. J., & Highfield, D. A. (1991). Extracellular characteristics of putative cholinergic neurons in the rat laterodorsal tegmental nucleus: Brain Research Vol 559(1) Sep 1991, 64-74.
- Greba, Q., Munro, L. J., & Kokkinidis, L. (2000). The involvement of ventral tegmental area cholinergic muscarinic receptors in classically conditioned fear expression as measured with fear-potentiated startle: Brain Research Vol 870(1-2) Jul 2000, 135-141.
- Greenshaw, A. J. (1993). Differential effects of ondansetron, haloperidol and clozapine on electrical self-stimulation of the ventral tegmental area: Behavioural Pharmacology Vol 4(5) Oct 1993, 479-485.
- Grottick, A. J., Montgomery, A. M. J., & Herberg, L. J. (1997). Rapid recovery of self-stimulation from depression produced by the atypical neuroleptic risperidone is not prevented by 5-HT-sub-2 receptor stimulation: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 58(4) Dec 1997, 1045-1049.
- Grubb, M. C., Welch, J. R., Finn, D. A., & Mark, G. P. (2002). Cocaine self-administration alters the locomotor response to microinjection of bicuculline into the ventral tegmental area of rats: Brain Research Vol 952(1) Oct 2002, 44-51.
- Grunwerg, B. S., Krein, H., & Krauthamer, G. M. (1992). Somatosensory input and thalamic projection of pedunculopontine tegmental neurons: Neuroreport: An International Journal for the Rapid Communication of Research in Neuroscience Vol 3(8) Aug 1992, 673-675.
- Guarraci, F. A., & Kapp, B. S. (1999). An electrophysiological characterization of ventral tegmental area dopaminergic neurons during differential Pavlovian fear conditioning in the awake rabbit: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 99(2) Mar 1999, 169-179.
- Guitart, X., Lumeng, L., Li, T.-k., & Nestler, E. J. (1993). Alcohol-preferring and nonpreferring rats display different levels of neurofilament proteins in the ventral tegmental area: Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research Vol 17(3) Jun 1993, 580-585.
- Gulia, K. K., Mallick, H. N., & Kumar, V. M. (2004). Sleep-related penile erections do not occur in rats during carbachol-induced rapid eye movement sleep: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 154(2) Oct 2004, 585-587.
- Hahmann, U., & Gunturkun, O. (1992). Visual-discrimination deficits after lesions of the centrifugal visual system in pigeons (Columba livia): Visual Neuroscience Vol 9(3-4) Sep-Oct 1992, 225-233.
- Hamann, S. R., & Martin, W. R. (1992). Analgesic actions of dynorphin A(1-23) antiserum in the rat brain stem: Brain Research Bulletin Vol 29(5) Nov 1992, 605-607.
- Hamann, S. R., & Martin, W. R. (1994). Hyperalgesic and analgesic actions of morphine, U50-488, naltrexone, and (-)-lobeline in the rat brainstem: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 47(1) Jan 1994, 197-201.
- Hara, E., Kubikova, L., Hessler, N. A., & Jarvis, E. D. (2007). Role of the midbrain dopaminergic system in modulation of vocal brain activation by social context: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 25(11) Jun 2007, 3406-3416.
- Harris, G. C., & Aston-Jones, G. (2003). Critical role for ventral tegmental glutamate in preference for a cocaine-conditioned environment: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 28(1) Jan 2003, 73-76.
- Harris, H. W., & Nestler, E. J. (1988). Immunohistochemical studies of mesolimbic dopaminergic neurons in Fischer 344 and Lewis rats: Brain Research Vol 464 1988, 1-12.
- Harris, H. W., & Nestler, E. J. (1996). Immunohistochemical studies of mesolimbic dopaminergic neurons in Fischer 344 and Lewis rats: Brain Research Vol 706(1) Jan 1996, 1-12.
- Harte, M., & O'Connor, W. T. (2004). Evidence for a differential medial prefrontal dopamine D-sub-1 and D-sub-2 receptor regulation of local and ventral tegmental glutamate and GABA release: A dual probe microdialysis study in the awake rat: Brain Research Vol 1017(1-2) Aug 2004, 120-129.
- Hasegawa, T., Takeo, T., Akitsu, H., Hoshina, Y., & et al. (1991). Interruption of the lordosis reflex of female rats by ventral midbrain stimulation: Physiology & Behavior Vol 50(5) Nov 1991, 1033-1038.
- Hebb, A. L. O., Zacharko, R. M., & Anisman, H. (1998). Self-stimulation from the mesencephalon following intraventricular interleukin-2 administration: Brain Research Bulletin Vol 45(6) 1998, 549-556.
- Hedberg, C. E. (1993). Aggressive behavior in cats during different behavioral states following pontine tegmental lesions: Dissertation Abstracts International.
- Heidbreder, C., Gewiss, M., Lallemand, S., Roques, B. P., & et al. (1992). Inhibition of enkephalin metabolism and activation of mu- or delta-opioid receptors elicit opposite effects on reward and motility in the ventral mesencephalon: Neuropharmacology Vol 31(3) Mar 1992, 293-298.
- Henry, D. J., Hu, X.-T., & White, F. J. (1998). Adaptations in the mesoaccumbens dopamine system resulting from repeated adminisration of dopamine D-sub-1 and D-sub-2 receptor-selective agonists: Relevance to cocaine sensitization: Psychopharmacology Vol 140(2) Nov 1998, 233-242.
- Henry, D. J., Wise, R. A., Rompre, P.-P., & White, F. J. (1992). Acute depolarization block of A10 dopamine neurons: Interactions of morphine with dopamine antagonists: Brain Research Vol 596(1-2) Nov 1992, 231-237.
- Hernandez-Gonzalez, M., Guevara, M. A., Morali, G., & Cervantes, M. (1997). Subcortical multiple unit activity changes during rat male sexual behavior: Physiology & Behavior Vol 61(2) Feb 1997, 285-291.
- Hernandez-Gonzalez, M., Navarro-Meza, M., Prieto-Beracoechea, C. A., & Guevara, M. A. (2005). Electrical activity of prefrontal cortex and ventral tegmental area during rat maternal behavior: Behavioural Processes Vol 70(2) Sep 2005, 132-143.
- Hernandez-Gonzalez, M., Prieto-Beracoechea, C., Navarro-Meza, M., Ramos-Guevara, J. P., Reyes-Cortes, R., & Guevara, M. A. (2005). Prefrontal and tegmental electrical activity during olfactory stimulation in virgin and lactating rats: Physiology & Behavior Vol 83(5) Jan 2005, 749-758.
- Hildebrand, B. E., Panagis, G., Svensson, T. H., & Nomikos, G. G. (1999). Behavioral and biochemical manifestations of mecamylamine-precipitated nicotine withdrawal in the rat: Role of nicotinic receptors in the ventral tegmental area: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 21(4) Oct 1999, 560-574.
- Hillegaart, V., Magnusson, O., & Ahlenius, S. (2000). A9 and A10 dopamine nuclei as a site of action for effects of 8-OH-DPAT on locomotion in the rat: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 67(1) Sep 2000, 55-63.
- Ho, A., & Blum, M. (1998). Induction of interleukin-1 associated with compensatory dopaminergic sprouting in the denervated striatum of young mice: Model of aging and neurodegenerative disease: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 18(15) Aug 1998, 5614-5629.
- Hodge, C. W., Haraguchi, M., Chappelle, A. M., & Samson, H. H. (1996). Effects of ventral tegmental microinjections of the GABA-sub(A ) agonist muscimol on self-administration of ethanol and sucrose: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 53(4) Apr 1996, 971-977.
- Hodge, C. W., Haraguchi, M., Erickson, H. L., & Samson, H. H. (1993). Ventral tegmental microinjections of quinpirole decrease ethanol and sucrose-reinforced responding: Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research Vol 17(2) Apr 1993, 370-375.
- Homs-Ormo, S., Coll-Andreu, M., Satorra-Marin, N., Arevalo-Garcia, R., & Morgado-Bernal, I. (2003). Effects of pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus lesions on emotional reactivity and locomotion in rats: Brain Research Bulletin Vol 59(6) Feb 2003, 495-503.
- Homs-Ormo, S., Torras-Garcia, M., Portell-Cortes, I., Edo-Izquierdo, S., Morgado-Bernal, I., & Coll-Andreu, M. (2007). Effects of Posttraining Damage to the Pedunculopontine Tegmental Nucleus on Conditioned Stimulus Transfer in Two-Way Active Avoidance in Rats: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 121(2) Apr 2007, 411-421.
- Hooks, M. S., & Kalivas, P. W. (1994). Involvement of dopamine and excitatory amino acid transmission in novelty-induced motor activity: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 269(3) Jun 1994, 976-988.
- Hoplight, B. J., Vincow, E. S., & Neumaier, J. F. (2005). The effects of SB 224289 on anxiety and cocaine-related behaviors in a novel object task: Physiology & Behavior Vol 84(5) Apr 2005, 707-714.
- Horner, R. L., Sanford, L. D., Annis, D., Pack, A. I., & Morrison, A. R. (1997). Serotonin at the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus suppresses rapid-eye-movement sleep in freely behaving rats: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 17(19) Oct 1997, 7541-7552.
- Ikemoto, S. (2004). Unconditional hyperactivity and transient reinforcing effects of NMDA administration into the ventral tegmental area in rats: Psychopharmacology Vol 172(2) Mar 2004, 202-210.
- Ikemoto, S., Murphy, J. M., & McBride, W. J. (1997). Self-infusion of GABA-sub(A ) antagonists directly into the ventral tegmental area and adjacent regions: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 111(2) Apr 1997, 369-380.
- Ikemoto, S., Murphy, J. M., & McBride, W. J. (1998). Regional differences within the rat ventral tegmental area for muscimol self-infusions: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 61(1) Sep 1998, 87-92.
- Ikemoto, S., Witkin, B. M., & Morales, M. (2003). Rewarding injections of cholinergic agonist carbachol into the ventral tegmental area induce locomotion and c-Fos expression in the retrosplenial area and supramammillary nucleus: Brain Research Vol 969(1-2) Apr 2003, 78-87.
- Ikemoto, S., Witkin, B. M., Zangen, A., & Wise, R. A. (2004). Rewarding Effects of AMPA Administration into the Supramammillary or Posterior Hypothalamic Nuclei But Not the Ventral Tegmental Area: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 24(25) Jun 2004, 5758-5765.
- Inglis, W. L., Olmstead, M. C., & Robbins, T. W. (2000). Pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus lesions impair stimulus-reward learning in autoshaping and conditioned reinforcement paradigms: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 114(2) Apr 2000, 285-294.
- Inoue, M., Mishina, M., & Ueda, H. (2003). Locus-Specific Rescue of GluRepsilon l NMDA Receptors in Mutant Mice Identifies the Brain Regions Important for Morphine Tolerance and Dependence: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 23(16) Aug 2003, 6529-6536.
- Isobe, Y., & Nishino, H. (2001). Circadian rhythm of drinking and running-wheel activity in rats with 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the ventral tegmental area: Brain Research Vol 899(1-2) Apr 2001, 187-192.
- Itoi, K., Jost, N., Culman, J., Tschope, C., & et al. (1994). Further localization of cardiovascular and behavioral actions of substance P in the rat brain: Brain Research Vol 668(1-2) Dec 1994, 100-106.
- Ivanova, S., & Greenshaw, A. J. (1997). Nicotine-induced decreases in VTA electrical self-stimulation thresholds: Blockade by haloperidol and mecamylamine but not scopolamine or ondansetron: Psychopharmacology Vol 134(2) Nov 1997, 187-192.
- Jaeger, T. V., & van der Kooy, D. (1996). Separate neural substrates mediate the motivating and discriminative properties of morphine: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 110(1) Feb 1996, 181-201.
- Jay, T. M., Glowinski, J., & Thierry, A. M. (1995). Inhibition of hippocampo-prefrontal cortex excitatory responses by the mesocortical DA system: Neuroreport: An International Journal for the Rapid Communication of Research in Neuroscience Vol 6(14) Oct 1995, 1845-1848.
- Jerlhag, E., Grotli, M., Luthman, K., Svensson, L., & Engel, J. A. (2006). Role of the subunit composition of central nicotinic acetylcholine receptors for the stimulatory and dopamine-enhancing effects of ethanol: Alcohol and Alcoholism Vol 41(5) Sep-Oct 2006, 486-493.
- Johnson, J. H., Zhao, C., James, J. R., & Rosecrans, J. A. (2000). Individual variability of dopamine release from nucleus accumbens induced by nicotine: Brain Research Bulletin Vol 51(3) Feb 2000, 249-253.
- Johnson, K., Churchill, L., Klitenick, M. A., Hooks, M. S., & et al. (1996). Involvement of the ventral tegmental area in locomotion elicited from the nucleus accumbens or ventral pallidum: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 277(2) May 1996, 1122-1131.
- Jones, S., & Gutlerner, J. L. (2002). Addictive drugs modify excitatory synaptic control of midbrain dopamine cells: Neuroreport: For Rapid Communication of Neuroscience Research Vol 13(2) Feb 2002, A29-A33.
- Jones, S., Kornblum, J. L., & Kauer, J. A. (2000). Amphetamine blocks long-term synaptic depression in the ventral tegmental area: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 20(15) Aug 2000, 5575-5580.
- Jurkowlaniec, E., Tokarski, J., & Trojniar, W. (2003). Effect of unilateral ibotenate lesions of the ventral tegmental area on cortical and hippocampal EEG in freely behaving rats: Acta Neurobiologiae Experimentalis Vol 63(4) 2003, 369-375.
- Kalivas, P. W. (1993). Neurotransmitter regulation of dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area: Brain Research Reviews Vol 18(1) Jan-Apr 1993, 75-113.
- Kalivas, P. W. (1994). Blockade of neurotensin-induced motor activity by inhibition of protein kinase: Psychopharmacology Vol 114(1) Feb 1994, 175-180.
- Kalivas, P. W., & Duffy, P. (1995). D-sub-1 receptors modulate glutamate transmission in the ventral tegmental area: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 15(7, Pt 2) Jul 1995, 5379-5388.
- Kandov, Y., Israel, Y., Kest, A., Dostova, I., Verasammy, J., Bernal, S. Y., et al. (2006). GABA receptor subtype antagonists in the nucleus accumbens shell and ventral tegmental area differentially alter feeding responses induced by deprivation, glucoprivation and lipoprivation in rats: Brain Research Vol 1082(1) Apr 2006, 86-97.
- Kareken, D. A., Claus, E. D., Sabri, M., Dzemidzic, M., Kosobud, A. E. K., Radnovich, A. J., et al. (2004). Alcohol-related olfactory cues activate the nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmental area in high-risk drinkers: Preliminary findings: Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research Vol 28(4) Apr 2004, 550-557.
- Kauer, J. A. (2004). Learning Mechanisms in Addiction: Synaptic Plasticity in the Ventral Tegmental Area as a Result of Exposure to Drugs of Abuse: Annual Review of Physiology Vol 66 Mar 2004, 447-475.
- Keating, G. L., Walker, S. C., & Winn, P. (2002). An examination of the effects of bilateral excitotoxic lesions of the pedunculopotine tegmental nucleus on responding to sucrose reward: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 134(1-2) Aug 2002, 217-228.
- Kelley, A. E., & Delfs, J. M. (1991). Dopamine and conditioned reinforcement: II. Contrasting effects of amphetamine microinjection into the nucleus accumbens with peptide microinjection into the ventral tegmental area: Psychopharmacology Vol 103(2) Feb 1991, 197-203.
- Kelley, S. P., & Mittleman, G. (1999). Effects of hippocampal damage on reward threshold and response rate during self-stimulation of the ventral tegmental area in the rat: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 99(2) Mar 1999, 133-141.
- Kenny, P. J., Gasparini, F., & Markou, A. (2003). Group II Metabotropic and alpha -Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole Propionate (AMPA)/Kainate Glutamate Receptors Regulate the Deficit in Brain Reward Function Associated with Nicotine Withdrawal in Rats: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 306(3) Sep 2003, 1068-1076.
- Kentner, A. C., James, J. S., Miguelez, M., & Bielajew, C. (2007). Investigating the hedonic effects of interferon-alpha on female rats using brain-stimulation reward: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 177(1) Feb 2007, 90-99.
- Khaimova, E., Kandov, Y., Israel, Y., Cataldo, G., Hadjimarkou, M. M., & Bodnar, R. J. (2004). Opioid receptor subtype antagonists differentially alter GABA agonist-induced feeding elicited from either the nucleus accumbens shell or ventral tegmental area regions in rats: Brain Research Vol 1026(2) Nov 2004, 284-294.
- Kim, J.-H. (1998). Contribution of metabotropic glutamate receptors to the locomotor effects produced by acute and repeated injections of amphetamine. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Kimmel, H. L., Gong, W., Vechia, S. D., Hunter, R. G., & Kuhar, M. J. (2000). Intra-ventral tegmental area injection of rat cocaine and amphetamine-regulated transcript peptide 55-102 induces locomotor activity and promotes conditioned place preference: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 294(2) Aug 2000, 784-792.
- Kippin, T. E., & van der Kooy, D. (2003). Excitotoxic lesions of the tegmental pedunculopontine nucleus impair copulation in naive male rats and block the rewarding effects of copulation in experienced male rats: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 18(9) Nov 2003, 2581-2591.
- Kita, T., Okamoto, M., & Nakashima, T. (1992). Nicotine-induced sensitization to ambulatory stimulant effect produced by daily administration into the ventral tegmental area and the nucleus accumbens in rats: Life Sciences Vol 50(8) 1992, 583-590.
- Kiyatkin, E. A., & Rebec, G. V. (1997). Activity of presumed dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area during heroin self-administration: Neuroreport: An International Journal for the Rapid Communication of Research in Neuroscience Vol 8(11) Jul 1997, 2581-2585.
- Klitenick, M. A., De Witte, P., & Kalivas, P. W. (1992). Regulation of somatodendritic dopamine release in the ventral tegmental area by opioids and GABA: An in vivo microdialysis study: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 12(7) Jul 1992, 2623-2632.
- Klop, E. M., Mouton, L. J., & Holstege, G. (2006). Periparabigeminal and adjoining mesencephalic tegmental field projections to the dorsolateral periaqueductal grey in cat--A possible role for oculomotor input in the defensive system: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 23(8) Apr 2006, 2145-2157.
- Kobayashi, Y., Inoue, Y., Yamamoto, M., Isa, T., & Aizawa, H. (2002). Contribution of Pedunculopontine Tegmental Nucleus Neurons to Performance of Visually Guided Saccade Tasks in Monkeys: Journal of Neurophysiology Vol 88(2) Aug 2002, 715-731.
- Kojima, Y., Yoshida, K., & Iwamoto, Y. (2007). Microstimulation of the midbrain tegmentum creates learning signals for saccade adaptation: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 27(14) Apr 2007, 3759-3767.
- Kokkinidis, L., & Borowski, T. B. (1991). Sensitization of mesolimbic brain stimulation reward after electrical kindling of the amygdala: Brain Research Bulletin Vol 27(6) Dec 1991, 791-796.
- Korotkova, T. M., Brown, R. E., Sergeeva, O. A., Ponomarenko, A. A., & Haas, H. L. (2006). Effects of arousal- and feeding-related neuropeptides on dopaminergic and GABAergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area of the rat: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 23(10) May 2006, 2677-2685.
- Korotkova, T. M., Sergeeva, O. A., Eriksson, K. S., Haas, H. L., & Brown, R. E. (2003). Excitation of Ventral Tegmental Area Dopaminergic and Nondopaminergic Neurons by Orexins/Hypocretins: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 23(1) Jan 2003, 7-11.
- Kosobud, A. E. K., Harris, G. C., & Chapin, J. K. (1994). Behavioral associations of neuronal activity in the ventral tegmental area of the rat: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 14(11, Pt 2) Nov 1994, 7117-7129.
- Koyama, S., & Appel, S. B. (2006). Characterization of M-Current in Ventral Tegmental Area Dopamine Neurons: Journal of Neurophysiology Vol 96(2) Aug 2006, 535-543.
- Koyama, S., & Appel, S. B. (2006). A-type K-super(+) Current of Dopamine and GABA Neurons in the Ventral Tegmental Area: Journal of Neurophysiology Vol 96(2) Aug 2006, 544-554.
- Kreider, J. C. (2004). The neural substrates of active sleep in infant rats. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Lamonte, N., Echo, J. A., Ackerman, T. F., Christian, G., & Bodnar, R. J. (2002). Analysis of opioid receptor subtype antagonist effects upon mu opioid agonist-induced feeding elicited from the ventral tegmental area of rats: Brain Research Vol 929(1) Mar 2002, 96-100.
- Landeira-Fernandez, J., & Grijalva, C. V. (2004). Participation of the substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons in the occurrence of gastric mucosal erosions: Physiology & Behavior Vol 81(1) Mar 2004, 91-99.
- Larsson, A., Edstrom, L., Svensson, L., Soderpalm, B., & Engel, J. A. (2005). Voluntary ethanol intake increases extracellular acetylcholine levels in the ventral tegmental area in the rat: Alcohol and Alcoholism Vol 40(5) Sep-Oct 2005, 349-358.
- Larsson, A., & Engel, J. A. (2004). Neurochemical and behavioral studies on ethanol and nicotine interactions: Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews Vol 27(8) Jan 2004, 713-720.
- Laviolette, S. R., Alexson, T. O., & van der Kooy, D. (2002). Lesions of the Tegmental Pedunculopontine Nucleus Block the Rewarding Effects and Reveal the Aversive Effects of Nicotine in the Ventral Tegmental Area: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 22(19) Oct 2002, 8653-8660.
- Laviolette, S. R., Gallegos, R. A., Henriksen, S. J., & van der Kooy, D. (2004). Opiate state controls bi-directional reward signaling via GABAasymptotic-to > receptors in the ventral tegmental area: Nature Neuroscience Vol 7(2) Feb 2004, 160-169.
- Laviolette, S. R., & Kooy, D. (2003). The motivational valence of nicotine in the rat ventral tegmental area is switched from rewarding to aversive following blockade of the alpha 7-subunit-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: Psychopharmacology Vol 166(3) Mar 2003, 306-313.
- Laviolette, S. R., Priebe, R. P. M., & Yeomans, J. S. (2000). Role of the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus in scopolamine- and amphetamine-induced locomotion and stereotypy: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 65(1) Jan 2000, 163-174.
- Laviolette, S. R., & van der Kooy, D. (2001). GABA receptors in the ventral tegmental area control bidirectional reward signalling between dopaminergic and non-dopaminergic neural motivational systems: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 13(5) Mar 2001, 1009-1015.
- Laviolette, S. R., & van der Kooy, D. (2003). Blockade of mesolimbic dopamine transmission dramatically increases sensitivity to the rewarding effects of nicotine in the ventral tegmental area: Molecular Psychiatry Vol 8(1) 2003, 50-59.
- Laviolette, S. R., & van der Kooy, D. (2004). The neurobiology of nicotine addiction: Bridging the gap from molecules to behaviour: Nature Reviews Neuroscience Vol 5(1) Jan 2004, 55-65.
- Leaton, R. N. (2003). Electrolytic, but not neurotoxic, lesions to the lateral tegmental tract increase acoustic startle amplitude and reduce startle stimulus-induced freezing: Neurobiology of Learning and Memory Vol 79(1) Jan 2003, 89-98.
- Lee, D. Y., Guttilla, M., Fung, K. D., McFeron, S., Yan, J., & Ranaldi, R. (2007). Rostral--Caudal differences in the effects of intra-VTA muscimol on cocaine self-administration: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 86(3) Mar 2007, 542-549.
- Lee, R.-S., Steffensen, S. C., & Henriksen, S. J. (2001). Discharge profiles of ventral tegmental area GABA neurons during movement, anesthesia, and the sleep-wake cycle: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 21(5) Mar 2001, 1757-1766.
- Lee, Y.-K., Park, S.-W., Kim, Y.-K., Kim, D.-J., Jeong, J., Myrick, H., et al. (2005). Effects of naltrexone on the ethanol-induced changes in the rat central dopaminergic system: Alcohol and Alcoholism Vol 40(4) Jul-Aug 2005, 297-301.
- Leite-Morris, K. A., Fukudome, E. Y., Shoeb, M. H., & Kaplan, G. B. (2004). GABA-sub(B) Receptor Activation in the Ventral Tegmental Area Inhibits the Acquisition and Expression of Opiate-Induced Motor Sensitization: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 308(2) Feb 2004, 667-678.
- Lepore, M. (1995). Parametric and neurological studies of brain stimulation reward. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Leri, F. (2001). Analysis of behavioral deficits induced by pedunculopontine tegmental lesions. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Leri, F., & Franklin, K. B. J. (1998). Learning impairments caused by lesions to the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus: An artifact of anxiety? : Brain Research Vol 807(1-2) Oct 1998, 187-192.
- Leri, F., & Franklin, K. B. J. (2000). Diazepam modifies the effect of pedunculopontine lesions on morphine but not on amphetamine conditioned place preference: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 117(1-2) Dec 2000, 21-27.
- Leszkowicz, E., & Trojniar, W. (2005). Activation of tachykinin system in the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus suppresses hippocampal theta rhythm in urethane-anesthetized rats: Acta Neurobiologiae Experimentalis Vol 65(4) 2005, 373-386.
- Levin, E. D., Briggs, S. J., Christopher, N. C., & Auman, J. T. (1994). Working memory performance and cholinergic effects in the ventral tegmental area and substantia nigra: Brain Research Vol 657(1-2) Sep 1994, 165-170.
- Lewis, B., & O'Donnell, P. (2003). Blockade of the GlyT1 Glycine Transporter Prolongs Response to VTA Stimulation in Nucleus Accumbens Neurons. New York, NY: New York Academy of Sciences.
- Licata, S. C., Freeman, A. Y., Pierce-Bancroft, A. F., & Pierce, R. C. (2000). Repeated stimulation of L-type calcium channels in the rat ventral tegmental area mimics the initiation of behavioral sensitization to cocaine: Psychopharmacology Vol 152(1) Sep 2000, 110-118.
- Licata, S. C., Schmidt, H. D., & Pierce, R. C. (2004). Suppressing calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity in the ventral tegmental area enhances the acute behavioural response to cocaine but attenuates the initiation of cocaine-induced behavioural sensitization in rats: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 19(2) Jan 2004, 405-414.
- Linderholm, K. R., Andersson, A., Olsson, S., Olsson, E., Snodgrass, R., Engberg, G., et al. (2007). Activation of rat ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons by endogenous kynurenic acid: A pharmacological analysis: Neuropharmacology Vol 53(8) Dec 2007, 918-924.
- Liu, W., Thielen, R. J., Rodd, Z. A., & McBride, W. J. (2006). Activation of serotonin-3 receptors increases dopamine release within the ventral tegmental area of Wistar and alcohol-preferring (P) rats: Alcohol Vol 40(3) Nov 2006, 167-176.
- Liu, Z.-H., & Jin, W.-Q. (2004). Decrease of ventral tegmental area dopamine neuronal activity in nicotine withdrawal rats: Neuroreport: For Rapid Communication of Neuroscience Research Vol 15(9) Jun 2004, 1479-14781.
- Lodge, D. J., & Grace, A. A. (2005). Acute and Chronic Corticotropin-Releasing Factor 1 Receptor Blockade Inhibits Cocaine-Induced Dopamine Release: Correlation with Dopamine Neuron Activity: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 314(1) Jul 2005, 201-206.
- Lodge, D. J., Grace, A. A., & Palmiter, R. D. (2006). The laterodorsal tegmentum is essential for burst firing of ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons: PNAS Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America Vol 103(13) Mar 2006, 5167-5172.
- Lof, E., Olausson, P., de Bejczy, A., Stomberg, R., McIntosh, J. M., Taylor, J. R., et al. (2007). Nicotonic acetylcholine receptors in the ventral tegmental area mediate the dopamine activating and reinforcing properties of ethanol cues: Psychopharmacology Vol 195(3) Dec 2007, 333-343.
- Louis, M., & Clarke, P. B. S. (1998). Effect of ventral tegmental 6-hydroxydopamine lesions on the locomotor stimulant action of nicotine in rats: Neuropharmacology Vol 37(12) Dec 1998, 1503-1513.
- Lu, C. C., Tseng, C. J., Wan, F. J., Yin, T. H., & et al. (1992). Role of locus coeruleus and serotonergic drug actions on schedule-induced polydipsia: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 43(1) Sep 1992, 255-261.
- Lu, L., Dempsey, J., Liu, S. Y., Bossert, J. M., & Shaham, Y. (2004). A Single Infusion of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor into the Ventral Tegmental Area Induces Long-Lasting Potentiation of Cocaine Seeking after Withdrawal: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 24(7) Feb 2004, 1604-1611.
- Lu, W., Monteggia, L. M., & Wolf, M. E. (2002). Repeated administration of amphetamine or cocaine does not alter AMPA receptor subunit expression in the rat midbrain: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 26(1) Jan 2002, 1-13.
- Luebke, J. I., McCarley, R. W., & Greene, R. W. (1993). Inhibitory action of muscarinic agonists on neurons in the rat laterodorsal tegmental nucleus in vitro: Journal of Neurophysiology Vol 70(5) Nov 1993, 2128-2135.
- Maillard, C.-A., & Edwards, D. A. (1991). Excitotoxin lesions of the zona incerta/lateral tegmentum continuum: Effects of male sexual behavior in rats: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 46(2) Dec 1991, 143-149.
- Maldonado, R., Valverde, O., & Berrendero, F. (2006). Involvement of the endocannabinoid system in drug addiction: Trends in Neurosciences Vol 29(4) Apr 2006, 225-232.
- Malette, J., & Miliaressis, E. (1995). Interhemispheric links in brain stimulation reward: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 68(2) Jun 1995, 117-137.
- Maliszewska-Scislo, M., & Trojniar, W. (1999). Augmentation of ventral tegmental area stimulation-induced feeding by both stimulation and lesion of the contralateral ventral tegmental area in the rat: Acta Neurobiologiae Experimentalis Vol 59(4) 1999, 287-293.
- Maloney, K. J., Mainville, L., & Jones, B. E. (2002). c-Fos expression in dopaminergic and GABAergic neurons of the ventral mesencephalic tegmentum after parodoxical sleep deprivation and recovery: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 15(4) Feb 2002, 774-778.
- Manzoni, O. J., & Williams, J. T. (1999). Presynaptic regulation of glutamate release in the ventral tegmental area during morphine withdrawal: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 19(15) Aug 1999, 6629-6636.
- Margolis, E. B., Hjelmstad, G. O., Bonci, A., & Fields, H. L. (2003). kappa -Opioid Agonists Directly Inhibit Midbrain Dopaminergic Neurons: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 23(31) Nov 2003, 9981-9986.
- Margolis, E. B., Lock, H., Chefer, V. I., Shippenberg, T. S., Hjelmstad, G. O., & Fields, H. L. (2006). kappa opioids selectively control dopaminergic neurons projecting to the prefrontal cortex: PNAS Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America Vol 103(8) Feb 2006, 2938-2942.
- Martin, L. E. (2006). Impulsivity and neural systems of rewards. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Martin, L. E., & Potts, G. F. (2004). Reward sensitivity in impulsivity: Neuroreport: For Rapid Communication of Neuroscience Research Vol 15(9) Jun 2004, 1519-1522.
- Martinez-Hernandez, J., Lanuza, E., & Martinez-Garcia, F. (2006). Selective dopaminergic lesions of the ventral tegmental area impair preference for sucrose but not for male sexual pheromones in female mice: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 24(3) Aug 2006, 885-893.
- Masino, T. (1992). Brainstem control of orienting movements: Intrinsic coordinate systems and underlying circuitry: Brain, Behavior and Evolution Vol 40(2-3) Aug-Sep 1992, 98-111.
- Mathis, J., Hess, C. W., & Bassetti, C. (2007). Isolated mediotegmental lesion causing narcolepsy and rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder: A case evidencing a common pathway in narcolepsy and rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder: Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry Vol 78(4) Apr 2007, 427-429.
- Mathur, A., Shandarin, A., LaViolette, S. R., Parker, J., & Yeomans, J. S. (1997). Locomotion and stereotypy induced by scopolamine: Contributions of muscarinic receptors near the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus: Brain Research Vol 775(1-2) Nov 1997, 144-155.
- McClung, C. A., Sidiropoulou, K., Vitaterna, M., Takahashi, J. S., White, F. J., Cooper, D. C., et al. (2005). Regulation of dopaminergic transmission and cocaine reward by the Clock gene: PNAS Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America Vol 102(26) Jun 2005, 9377-9381.
- McFarland, K., Davidge, S. B., Lapish, C. C., & Kalivas, P. W. (2004). Limbic and Motor Circuitry Underlying Footshock-Induced Reinstatement of Cocaine-Seeking Behavior: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 24(7) Feb 2004, 1551-1560.
- Melis, M. R., Melis, T., Cocco, C., Succu, S., Sanna, F., Pillolla, G., et al. (2007). Oxytocin injected into the ventral tegmental area induces penile erection and increases extracellular dopamine in the nucleus accumbens and paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus of male rats: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 26(4) Aug 2007, 1026-1035.
- Mercuri, N. B., Calabresi, P., & Bernardi, G. (1992). The electrophysiological actions of dopamine and dopaminergic drugs on neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta and ventral tegmental area: Life Sciences Vol 51(10) 1992, 711-718.
- Metzner, W. (1993). An audio-vocal interface in echolocating horseshoe bats: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 13(5) May 1993, 1899-1915.
- Minabe, Y., Ashby, C. R., & Wang, R. Y. (1992). Effects produced by acute and chronic treatment with granisetron alone or in combination with haloperidol on midbrain dopamine neurons: European Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 2(2) Jun 1992, 127-133.
- Minabe, Y., Emori, K., & Ashby, C. R. (1995). Significant differences in the activity of midbrain dopamine neurons between male Fischer 344 (F344) and Lewis rats: An in vivo electrophysiological study: Life Sciences Vol 56(15) Mar 1995, PL 261-267.
- Miyata, H., Ando, K., & Yanagita, T. (2002). Brain regions mediating the discriminative stimulus effects of nicotine in rats. New York, NY: New York Academy of Sciences.
- Monti, J. M., & Jantos, H. (2004). Effects of the 5-HT1A receptor ligands flesinoxan and WAY 100635 given systemically or microinjected into the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus on REM sleep in the rat: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 151(1-2) May 2004, 159-166.
- Moore, H., Rose, H. J., & Grace, A. A. (2001). Chronic cold stress reduces the spontaneous activity of ventral tegmental dopamine neurons: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 24(4) Apr 2001, 410-419.
- Moreau, J.-L., Jenck, F., Martin, J. R., Mortas, P., & et al. (1992). Antidepressant treatment prevents chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced anhedonia as assessed by ventral tegmentum self-stimulation behavior in rats: European Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 2(1) Mar 1992, 43-49.
- Morikawa, H., Khodakhah, K., & Williams, J. T. (2003). Two Intracellular Pathways Mediate Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor-Induced Ca-super(2+) Mobilization in Dopamine Neurons: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 23(1) Jan 2003, 149-157.
- Morimoto, K. (2004). Progressive Nature on the Process of Functional Psychoses: Pathological Sensitization and Psychoplasticity: Seishin Igaku (Clinical Psychiatry) Vol 46(4) Apr 2004, 423-433.
- Morissette, M.-C., & Boye, S. M. (2008). Electrolytic lesions of the habenula attenuate brain stimulation reward: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 187(1) Feb 2008, 17-26.
- Morrow, B. A., Elsworth, J. D., Zito, C., & Roth, R. H. (1999). Biochemical and behavioral anxiolytic-like effects of R(+)HA-966 at the level of the ventral tegmental area in rats: Psychopharmacology Vol 143(3) Apr 1999, 227-234.
- Morutto, S. L., & Phillips, G. D. (1998). Interactions between intra-perifornical region sulpiride and intra-ventral tegmental area AP5 on measures of locomotor activity and conditioned place preference: Psychopharmacology Vol 136(2) Mar 1998, 105-113.
- Morzorati, S. L. (1998). VTA dopamine neuron activity distinguishes alcohol-preferring (P) rats from Wistar rats: Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research Vol 22(4) Jun 1998, 854-857.
- Munn, E. M. (2000). Effects of blockade of muscarinic receptors in the ventral tegmental area: Attenuation of cocaine reward, but enhancement of locomotor activity and dopamine overflow in the nucleus accumbens. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Munro, L. J., & Kokkinidis, L. (1997). Infusion of quinpirole and muscimol into the ventral tegmental area inhibits fear-potentiated startle: Implications for the role of dopamine in fear expression: Brain Research Vol 746(1-2) Jan 1997, 231-238.
- Murray, B., & Shizgal, P. (1991). Anterolateral lesions of the medial forebrain bundle increase the frequency threshold for self-stimulation of the lateral hypothalamus and ventral tegmental area in the rat: Psychobiology Vol 19(2) Jun 1991, 135-146.
- Murray, B., & Shizgal, P. (1994). Evidence implicating both slow- and fast-conducting fibers in the rewarding effect of medial forebrain bundle stimulation: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 63(1) Jul 1994, 47-60.
- Murray, B., & Shizgal, P. (1996). Behavioral measures of conduction velocity and refractory period for reward-relevant axons in the anterior LH and VTA: Physiology & Behavior Vol 59(4-5) Apr-May 1996, 643-652.
- Murray, B. M. (1994). The contribution of anterior medial forebrain bundle neurons to self-stimulation of the lateral hypothalamic and ventral tegmental areas. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Murschall, A., & Hauber, W. (2006). Inactivation of the ventral tegmental area abolished the general excitatory influence of Pavlovian cues on instrumental performance: Learning & Memory Vol 13(2) Mar-Apr 2006, 123-126.
- Museo, E., & Wise, R. A. (1994). Place preference conditioning with ventral tegmental injections of cytisine: Life Sciences Vol 55(15) 1994, 1179-1186.
- Museo, E., & Wise, R. A. (1994). Sensitization of locomotion following repeated ventral tegmental injections of cytisine: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 48(2) Jun 1994, 521-524.
- Museo, E., & Wise, R. A. (1995). Cytisine-induced behavioral activation: Delineation of neuroanatomical locus of action: Brain Research Vol 670(2) Jan 1995, 257-263.
- Myers, R. D., & Robinson, D. E. (1999). Tetrahydropapaveroline injected in the ventral tegmental area shifts dopamine efflux differentially in the shell and core of nucleus accumbens in high-ethanol-preferring (HEP) rats: Alcohol Vol 18(1) May 1999, 83-90.
- Myers, R. E. (1964). Visual deficits after lesions of brain stem tegmentum in cats: Archives of Neurology 11(1) 1964, 73-90.
- Mylecharane, E. J. (1995). Ventral tegmental area 5-HT receptors: Mesolimbic dopamine release and behavioural studies: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 73(1-2) Dec 1995, 1-5.
- Nader, K., Bechara, A., Roberts, D. C. S., & van der Kooy, D. (1994). Neuroleptics block high- but not low-dose heroin place preferences: Further evidence for a two-system model of motivation: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 108(6) Dec 1994, 1128-1138.
- Nader, K., & LeDoux, J. (1999). Inhibition of the mesoamygdala dopaminergic pathway impairs the retrieval of conditioned fear associations: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 113(5) Oct 1999, 891-901.
- Nader, K., & van der Kooy, D. (1994). The motivation produced by morphine and food is isomorphic: Approaches to specific motivational stimuli are learned: Psychobiology Vol 22(1) Mar 1994, 68-76.
- Nair, H. P., & Gonzalez-Lima, F. (1999). Extinction of behavior in infant rats: Development of functional coupling between septal, hippocampal, and ventral tegmental regions: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 19(19) Oct 1999, 8646-8655.
- Nakahara, D. (2004). Influence of Nicotine on Brain Reward Systems: Study of Intracranial Self-Stimulation. New York, NY: New York Academy of Sciences.
- Nakamura, T., Uramura, K., Nambu, T., Yada, T., Goto, K., Yanagisawa, M., et al. (2000). Orexin-induced hyperlocomotion and stereotypy are mediated by the dopaminergic system: Brain Research Vol 873(1) Aug 2000, 181-187.
- Narayanan, S., Lam, H., Carroll, F. I., & Lutfy, K. (2004). Orphanin FQ/nociceptin suppresses motor activity through an action along the mesoaccumbens axis in rats: Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience Vol 29(2) Mar 2004, 116-123.
- Narayanan, S., Lutfy, K., & Maidment, N. (2002). Sensitization to cocaine after a single intra-cerebral injection of orphanin FQ/nociceptin: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 131(1-2) Apr 2002, 97-104.
- Narayanan, S., & Maidment, N. T. (1999). Orphanin FQ and behavioral sensitization to cocaine: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 63(2) Jun 1999, 271-277.
- Narayanan, S., Wallace, L., & Uretsky, N. (1996). Spontaneous and drug-stimulated locomotor activity after the administration of pertussis toxin into the ventral tegmental area: Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience Vol 21(3) May 1996, 172-180.
- Narayanan, S., Willins, D., Dalia, A., Wallace, L., & et al. (1996). Role of dopaminergic mechanisms in the stimulatory effects of MK-801 injected into the ventral tegmental area and the nucleus accumbens: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 54(3) Jul 1996, 565-573.
- Navailles, S., Moison, D., Cunningham, K. A., & Spampinato, U. (2008). Differential regulation of the mesoaccumbens dopamine circuit by serotonin2C receptors in the ventral tegmental area and the nucleus accumbens: An in vivo microdialysis study with cocaine: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 33(2) Jan 2008, 237-246.
- Nebes, R. D., Pollock, B. G., Meltzer, C. C., Saxton, J. A., Houck, P. R., Halligan, E. M., et al. (2005). Serum anticholinergic activity, white matter hyperintensities, and cognitive performance: Neurology Vol 65(9) Nov 2005, 1487-1489.
- Nencini, P., & Stewart, J. (1990). Chronic systemic administration of amphetamine increases food intake to morphine, but not to U50-488H, microinjected into the ventral tegmental area in rats: Brain Research Vol 527(2) Sep 1990, 254-258.
- Nikulina, E. M., Miczek, K. A., & Hammer, R. P., Jr. (2005). Prolonged Effects of Repeated Social Defeat Stress on mRNA Expression and Function of mu -Opioid Receptors in the Ventral Tegmental Area of Rats: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 30(6) Jun 2005, 1096-1103.
- Ninomiya, Y., Kayama, Y., & Koyama, Y. (2005). Postnatal development of cholinergic neurons in the mesopontine tegmentum revealed by histochemistry: International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience Vol 23(8) Dec 2005, 711-721.
- No authorship, i. (1989). The Mesocorticolimbic Dopamine System: Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. Vol. 537: PsycCRITIQUES Vol 34 (10), Oct, 1989.
- Noel, M. B. (1993). The effect of opiate injections into the ventral tegmental area on feeding: Dissertation Abstracts International.
- Noel, M. B., & Wise, R. A. (1993). Ventral tegmental injections of morphine but not U-50,488H enhance feeding in food-deprived rats: Brain Research Vol 632(1-2) Dec 1993, 68-73.
- Noel, M. B., & Wise, R. A. (1995). Ventral tegmental injections of a selective !m or !d opioid enhance feeding in food-deprived rats: Brain Research Vol 673(2) Mar 1995, 304-312.
- Nowak, K. L., McBride, W. J., Lumeng, L., Li, T. K., & Murphy, J. M. (2000). Involvement of dopamine D-sub-2 autoreceptors in the ventral tegmental area on alcohol and saccharin intake of the alcohol-preferring P rat: Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research Vol 24(4) Apr 2000, 476-483.
- Numan, M., & Numan, M. J. (1991). Preoptic)rainstem connections and maternal behavior in rats: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 105(6) Dec 1991, 1013-1029.
- Numan, M., & Numan, M. J. (1991). Preoptic-brainstem connections and maternal behavior in rats: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 105(6) Dec 1991, 1013-1029.
- Nuria, S.-M., Sandra, H.-O., Rosa, A.-G., Ignacio, M.-B., & Margalida, C.-A. (2005). Effects of pre-training pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus lesions on delayed matching- and non-matching-to-position in a T-maze in rats: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 160(1) May 2005, 115-124.
- O'Dell, L. E., & Parsons, L. H. (2004). Serotonin-sub(1B) Receptors in the Ventral Tegmental Area Modulate Cocaine-Induced Increases in Nucleus Accumbens Dopamine Levels: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 311(2) Nov 2004, 711-719.
- Olmstead, M. C., & Franklin, K. B. J. (1994). Lesions of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus block drug-induced reinforcement but not amphetamine-induced locomotion: Brain Research Vol 638(1-2) Feb 1994, 29-35.
- Olmstead, M. C., & Franklin, K. B. J. (1997). The development of a conditioned place preference to morphine: Effects of lesions of various CNS sites: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 111(6) Dec 1997, 1313-1323.
- Olmstead, M. C., & Franklin, K. B. J. (1997). The development of a conditioned place preference to morphine: Effects of microinjections into various CNS sites: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 111(6) Dec 1997, 1324-1334.
- Olmstead, M. C., Inglis, W. L., Bordeaux, C. P., Clarke, E. J., Wallum, N. P., Everitt, B. J., et al. (1999). Lesions of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus increase sucrose consumption but do not affect discrimination or contrast effects: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 113(4) Aug 1999, 732-743.
- Olmstead, M. C., Munn, E. M., Franklin, K. B. J., & Wise, R. A. (1998). Effects of pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus lesions on responding for intravenous heroin under different schedules of reinforcement: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 18(13) Jul 1998, 5035-5044.
- Ortiz, J., Fitzgerald, L. W., Lane, S., Terwilliger, R., & Nestler, E. J. (1996). Biochemical adaptations in the mesolimbic dopamine system in response to repeated stress: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 14(6) Jun 1996, 443-452.
- Ostrowski, N. L., & Pert, A. (1995). Substantia nigra opiate receptors on basal ganglia efferents: Brain Research Bulletin Vol 38(6) 1995, 513-523.
- Paice, J. A. (1993). The role of the dorsolateral pontine tegmentum in modulating nociception: Dissertation Abstracts International.
- Pan, W.-X., & Hyland, B. I. (2005). Pedunculopontine Tegmental Nucleus Controls Conditioned Responses of Midbrain Dopamine Neurons in Behaving Rats: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 25(19) May 2005, 4725-4732.
- Panagis, G., & Kastellakis, A. (2002). The effects of ventral tegmental administration of GABA-sub(A), GABA-sub(B), NMDA and AMPA receptor agonists on ventral pallidum self-stimulation: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 131(1-2) Apr 2002, 115-124.
- Panagis, G., Kastellakis, A., & Spyraki, C. (1998). Involvement of the ventral tegmental area opiate receptors in self-stimulation elicited from the ventral pallidum: Psychopharmacology Vol 139(3) Oct 1998, 222-229.
- Panagis, G., Nisell, M., Nomikos, G. G., Chergui, K., & et al. (1996). Nicotine injections into the ventral tegmental area increase locomotion and Fos-like immunoreactivity in the nucleus accumbens of the rat: Brain Research Vol 730(1-2) Aug 1996, 133-142.
- Pananceau, M., Rispal-Padel, L., & Meftah, E. M. (1996). Synaptic plasticity of the interpositorubral pathway functionally related to forelimb flexion movements: Journal of Neurophysiology Vol 75(6) Jun 1996, 2542-2561.
- Panayi, F., Colussi-Mas, J., Lambas-Senas, L., Renaud, B., Scarna, H., & Berod, A. (2005). Endogenous Neurotensin in the Ventral Tegmental Area Contributes to Amphetamine Behavioral Sensitization: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 30(5) May 2005, 871-879.
- Panocka, I., Ciccocioppo, R., Polidori, C., & Massi, M. (1993). The nucleus accumbens is a site of action for the inhibitory effect of ritanserin on ethanol intake in rats: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 46(4) Dec 1993, 857-862.
- Parker, J. L., & van der Kooy, D. (1995). Tegmental pedunculopontine nucleus lesions do not block cocaine reward: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 52(1) Sep 1995, 77-83.
- Perugini, M., & Vezina, P. (1994). Amphetamine administered to the ventral tegmental area sensitized rats to the locomotor effects of nucleus accumbens amphetamine: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 270(2) Aug 1994, 690-696.
- Pessia, M., Jiang, Z.-G., North, R. A., & Johnson, S. W. (1994). Actions of 5-hydroxytryptamine on ventral tegmental area neurons of the rat in vitro: Brain Research Vol 654(2) Aug 1994, 324-330.
- Peters, Y. M., & O'Donnell, P. (2005). Social Isolation Rearing Affects Prefrontal Cortical Response to Ventral Tegmental Area Stimulation: Biological Psychiatry Vol 57(10) May 2005, 1205-1208.
- Petralia, S. M. (2007). In the ventral tegmental area, dopamine type 1 receptor-initiated intracellular signaling cascades mediate progestins' actions for lordosis of rodents. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Petralia, S. M., DeBold, J. F., & Frye, C. A. (2007). MK-801 infusions to the ventral tegmental area and ventromedial hypothalamus produce opposite effects on lordosis of hormone-primed rats: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 86(2) Feb 2007, 377-385.
- Petralia, S. M., & Frye, C. A. (2005). In the ventral tegmental area picrotoxin blocks FGIN 1-27-induced increases in sexual behavior of rats and hamsters: Psychopharmacology Vol 178(2-3) Mar 2005, 174-182.
- Petralia, S. M., & Frye, C. A. (2006). In the ventral tegmental area, G-proteins mediate progesterone's actions at dopamine type 1 receptors for lordosis of rats and hamsters: Psychopharmacology Vol 186(2) Jun 2006, 133-142.
- Petralia, S. M., Jahagirdar, V., & Frye, C. A. (2005). Inhibiting biosynthesis and/or metabolism of progestins in the ventral tegmental area attenuates lordosis of rats in behavioural oestrus: Journal of Neuroendocrinology Vol 17(9) Sep 2005, 545-552.
- Phillips, A. G., Ahn, S., & Howland, J. G. (2003). Amygdalar control of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system: Parallel pathways to motivated behavior: Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews Vol 27(6) Sep 2003, 543-554.
- Phillips, A. G., Coury, A., Fiorino, D., LePiane, F. G., Brown, E., & Fibiger, H. C. (1992). Self-stimulation of the ventral tegmental area enhances dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens: A microdialysis study. New York, NY: New York Academy of Sciences.
- Phillips, G. D., Robbins, T. W., & Everitt, B. J. (1994). Mesoaccumbens dopamine-opiate interactions in the control over behaviour by a conditioned reinforcer: Psychopharmacology Vol 114(2) Mar 1994, 345-359.
- Pidoplichko, V. I., Noguchi, J., Areola, O. O., Liang, Y., Peterson, J., Zhang, T., et al. (2004). Nicotinic cholinergic synaptic mechanisms in the ventral tegmental area contribute to nicotine addiction: Learning & Memory Vol 11(1) Jan-Feb 2004, 60-69.
- Pierce, R. C., Born, B., Adams, M., & Kalivas, P. W. (1996). Repeated intra-ventral tegmental area administration of SKF-38393 induces behavioral and neurochemical sensitization to a subsequent cocaine challenge: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 278(1) Jul 1996, 384-392.
- Piercey, M. F., Lum, J. T., Hoffmann, W. E., Carlsson, A., & et al. (1992). Antagonism of cocaine's pharmacological effects by the stimulant dopaminergic antagonists, (+)-AJ76 and (+)-UH232: Brain Research Vol 588(2) Aug 1992, 217-222.
- Pillolla, G., Melis, M., Perra, S., Muntoni, A. L., Gessa, G. L., & Pistis, M. (2007). Medial forebrain bundle stimulation evokes endocannabinoid-mediated modulation of ventral tegmental area dopamine neuron firing in vivo: Psychopharmacology Vol 191(3) Apr 2007, 843-853.
- Pitzer, M. R. (1999). The ventral tegmental area's role in locomotion elicited by infusing kainic acid into the hypothalamus. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Podhorna, J., & Franklin, K. B. J. (1998). Lesions of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus increase anxiety in rats: Neuroreport: An International Journal for the Rapid Communication of Research in Neuroscience Vol 9(8) Jun 1998, 1783-1786.
- Podhorna, J., & Franklin, K. B. J. (1999). Long-lasting increase in anxiety after electrolytic lesions of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 113(3) Jun 1999, 550-557.
- Podhorna, J., & Franklin, K. B. J. (2000). Pontine tegmentum lesions increase anxiety-like behavior in rats: A comparison with anxiety produced by beta -CCE: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 65(2) Feb 2000, 267-273.
- Poirier, C. C., De Volder, A. G., Tranduy, D., & Scheiber, C. (2006). Neural changes in the ventral and dorsal visual streams during pattern recognition learning: Neurobiology of Learning and Memory Vol 85(1) Jan 2006, 36-43.
- Porr, B., Kulvicius, T., & Worgotter, F. (2007). Improved stability and convergence with three factor learning: Neurocomputing: An International Journal Vol 70(10-12) Jun 2007, 2005-2008.
- Prieto-Gomez, B., Benitez, M. T., Vazquez-Alvarez, A. M., Yang, P. B., Vazquez, C. R., & Dafny, N. (2004). Dopaminergic ventral tegmental neurons modulated by methylphenidate: Life Sciences Vol 74(13) Feb 2004, 1581-1592.
- Przegalinski, E., Papla, I., Siwanowicz, J., & Filip, M. (2004). Effects of 5-HT-sub(1B) receptor ligands microinjected into the ventral tegmental area on the locomotor and sensitizating effects of cocaine in rats: European Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 14(3) May 2004, 217-225.
- Quertemont, E., Eriksson, C. J. P., Zimatkin, S. M., Pronko, P. S., Diana, M., Pisano, M., et al. (2005). Is Ethanol a Pro-Drug? Acetaldehyde Contribution to Brain Ethanol Effects: Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research Vol 29(8) Aug 2005, 1514-1521.
- Quertemont, E., Grant, K. A., Correa, M., Arizzi, M. N., Salamone, J. D., Tambour, S., et al. (2005). The Role of Acetaldehyde in the Central Effects of Ethanol: Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research Vol 29(2) Feb 2005, 221-234.
- Quinn, J. G., O'Hare, E., Levine, A. S., & Kim, E.-M. (2003). Evidence for a mu -opioid-opioid connection between the paraventricular nucleus and ventral tegmental area in the rat: Brain Research Vol 991(1-2) Nov 2003, 206-211.
- Rada, P. V., Mark, G. P., Yeomans, J. J., & Hoebel, B. G. (2000). Acetylcholine release in ventral tegmental area by hypothalamic self-stimulation, eating, and drinking: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 65(3) Mar 2000, 375-379.
- Ragnauth, A. K. (2001). Role of the nucleus accumbens in the mediation of opioid-induced feeding in rats. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Rajadhyaksha, A., Husson, I., Satpute, S. S., Kuppenbender, K. D., Ren, J. Q., Guerriero, R. M., et al. (2004). L-Type Ca-super(2+) Channels Mediate Adaptation of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2 Phosphorylation in the Ventral Tegmental Area after Chronic Amphetamine Treatment: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 24(34) Aug 2004, 7464-7476.
- Ranaldi, R., & Beninger, R. J. (1994). The effects of systemic and intracerebral injections of D-sub-1 and D-sub-2 agonists on brain stimulation reward: Brain Research Vol 651(1-2) Jul 1994, 283-292.
- Ranaldi, R., & Beninger, R. J. (1994). Rostral-caudal differences in effects of nucleus accumbens amphetamine on VTA ICSS: Brain Research Vol 642(1-2) Apr 1994, 251-258.
- Ranaldi, R., & Wise, R. A. (2001). Blockade of D1 dopamine receptors in the ventral tegmental area decreases cocaine reward: Possible role for dendritically released dopamine: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 21(15) Aug 2001, 5841-5846.
- Randall, W. L. (1964). The behavior of cats (Felis catus L.) with lesions in the caudal midbrain region: Behaviour, Leiden 23(1-2) 1964, 107-139.
- Rasmussen, K., & Czachura, J. F. (1995). Nicotine withdrawal leads to increased firing rates of midbrain dopamine neurons: Neuroreport: An International Journal for the Rapid Communication of Research in Neuroscience Vol 7(1) Dec 1995, 329-332.
- Rasmussen, K., Hsu, M.-A., & Yang, Y. (2007). The Orexin-1 receptor antagonist SB-334867 blocks the effects of antipsychotics on the activity of A9 and A10 dopamine neurons: Implications for antipsychotic therapy: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 32(4) Apr 2007, 786-792.
- Reuss, B., Dono, R., & Unsicker, K. (2003). Functions of Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF)-2 and FGF-5 in Astroglial Differentiation and Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability: Evidence from Mouse Mutants: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 23(16) Aug 2003, 6404-6412.
- Reynolds, S. M., Geisler, S., Berod, A., & Zahm, D. S. (2006). Neurotensin antagonist acutely and robustly attenuates locomotion that accompanies stimulation of a neurotensin-containing pathway from rostrobasal forebrain to the ventral tegmental area: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 24(1) Jul 2006, 188-196.
- Rodd, Z. A., Bell, R. L., McQueen, V. K., Davids, M. R., Hsu, C. C., Murphy, J. M., et al. (2005). Chronic Ethanol Drinking by Alcohol-Preferring Rats Increases the Sensitivity of the Posterior Ventral Tegmental Area to the Reinforcing Effects of Ethanol: Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research Vol 29(3) Mar 2005, 358-366.
- Rodd, Z. A., Bell, R. L., McQueen, V. K., Davids, M. R., Hsu, C. C., Murphy, J. M., et al. (2005). Prolonged Increase in the Sensitivity of the Posterior Ventral Tegmental Area to the Reinforcing Effects of Ethanol following Repeated Exposure to Cycles of Ethanol Access and Deprivation: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 315(2) Nov 2005, 648-657.
- Rodd, Z. A., Bell, R. L., Melendez, R. I., Kuc, K. A., Lumeng, L., Li, T.-K., et al. (2004). Comparison of Intracranial Self-Administration of Ethanol Within the Posterior Ventral Tegmental Area Between Alcohol-Preferring and Wistar Rats: Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research Vol 28(8) Aug 2004, 1212-1219.
- Rodd, Z. A., Bell, R. L., Zhang, Y., Murphy, J. M., Goldstein, A., Zaffaroni, A., et al. (2005). Regional Heterogeneity for the Intracranial Self-Administration of Ethanol and Acetaldehyde within the Ventral Tegmental Area of Alcohol-Preferring (P) Rats: Involvement of Dopamine and Serotonin: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 30(2) Feb 2005, 330-338.
- Rodd, Z. A., Gryszowka, V. E., Toalston, J. E., Oster, S. M., Ji, D., Bell, R. L., et al. (2007). The reinforcing actions of a serotonin-3 receptor agonist within the ventral tegmental area: Evidence for subregional and genetic differences and involvement of dopamine neurons: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 321(3) Jun 2007, 1003-1012.
- Rodd, Z. A., Melendez, R. I., Bell, R. L., Kuc, K. A., Zhang, Y., Murphy, J. M., et al. (2004). Intracranial Self-Administration of Ethanol within the Ventral Tegmental Area of Male Wistar Rats: Evidence for Involvement of Dopamine Neurons: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 24(5) Feb 2004, 1050-1057.
- Rodd-Henricks, Z. A., McKinzie, D. L., Crile, R. S., Murphy, J. M., & McBride, W. J. (2000). Regional heterogeneity for the intracranial self-administration of ethanol within the ventral tegmental area of female Wistar rats: Psychopharmacology Vol 149(3) Apr 2000, 217-224.
- Rodd-Henricks, Z. A., McKinzie, D. L., Melendez, R. I., Berry, N., Murphy, J. M., & McBride, W. J. (2003). Effects of serotonin-3 receptor antagonists on the intracranial self-administration of ethanol within the ventral tegmental area of Wistar rats: Psychopharmacology Vol 165(3) Jan 2003, 252-259.
- Rodd-Henricks, Z. A., Melendez, R. I., Zaffaroni, A., Goldstein, A., McBride, W. J., & Li, T.-K. (2002). The reinforcing effects of acetaldehyde in the posterior ventral tegmental area of alcohol-preferring rats: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 72(1-2) May 2002, 55-64.
- Rodrigues, R. W. P., Gomide, V. C., & Chadi, G. (2004). Astroglial and microglial activation in the Wistar rat ventral tegmental area after a single striatial injection of 6-hydroxydopamine: International Journal of Neuroscience Vol 114(2) Feb 2004, 197-216.
- Rodriguez-Landa, J. F., Contreras, C. M., Gutierrez-Garcia, A. G., & Bernal-Morales, B. (2003). Chronic, but not acute, clomipramine or fluoxetine treatment reduces the spontaneous firing rate in the mesoaccumbens neurons of the rat: Neuropsychobiology Vol 48(3) 2003, 116-123.
- Rodriguez-Manzo, G., & Pellicer, F. (2007). Electrical stimulation of the ventral tegmental area exerts opposite effects on male rat sexual behaviour expression depending on the stimulated sub region: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 179(2) May 2007, 310-313.
- Roland, B. L. (1991). Gastric mucosal erosions induced by lateral hypothalamic damage: Neuronal and dopaminergic mechanisms: Dissertation Abstracts International.
- Romero-Carbente, J. C., Camacho, F. J., & Paredes, R. G. (2006). The role of the dorsolateral tegmentum in the control of male sexual behavior: A reevaluation: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 170(2) May 2006, 262-270.
- Rompre, P.-P., & Gratton, A. (1992). A comparison of the effects of mesencephalic injections of neurotensin(1-23) and neuromedin N on brain electrical self-stimulation: Peptides Vol 13(4) Jul-Aug 1992, 713-719.
- Rompre, P.-P., & Gratton, A. (1993). Mesencephalic microinjections of neurotensin-(1-23) and its C-terminal fragment, neurotensin-(8-23), potentiate brain stimulation reward: Brain Research Vol 616(1-2) Jul 1993, 154-162.
- Rondini, T. A., de Crudis Rodrigues, B., de Oliveira, A. P., Bittencourt, J. C., & Elias, C. F. (2007). Melanin-concentrating hormone is expressed in the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus only in female rats: Brain Research Bulletin Vol 74(1-3) Sep 2007, 21-28.
- Rosenfield, M. E., & Moore, J. W. (1995). Connections to cerebellar cortex (Larsell's HVI) in the rabbit: A WGA-HRP study with implications for classical eyeblink conditioning: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 109(6) Dec 1995, 1106-1118.
- Ryou, J.-W., Cho, S.-Y., & Kim, H.-T. (1998). Lesion of the cerebellar interpositus nucleus or the red nucleus affects classically conditioned neuronal activity in the hippocampus: Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry Vol 22(1) Jan 1998, 169-185.
- Sahraei, H., Pirzadeh-Jahromi, G., Noorbakhshnia, M., Asgari, A., Haeri-Rohani, A., Khoshbaten, A., et al. (2004). Involvement of nucleus accumbens in i-arginine-induced conditioned place preference in rats: Behavioural Pharmacology Vol 15(7) Nov 2004, 473-480.
- Samoscanec, K., Futac, D. P., Samoscanec, S., & Topic, E. (2005). Brain effects of psychoactive substances: Alcoholism: Journal on Alcoholism and Related Addictions Vol 41(1) 2005, 43-51.
- Samson, H. H., & Chappell, A. M. (1999). Effects of microinjection of the D2 dopamine antagonist raclopride into the ventral tegmental area on ethanol and sucrose self-administration: Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research Vol 23(3) Mar 1999, 421-426.
- Sandner, G., Bielajew, C., & Fouriezos, G. (1996). Bicuculline microinjections into the ventral tegmental area of the rat: Alteration of self-stimulation thresholds and of cytochrome oxidase activity in the brain: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 79(1-2) Sep 1996, 145-151.
- Saponjic, J., Cvorovic, J., Radulovacki, M., & Carley, D. W. (2005). Serotonin and noradrenaline modulate respiratory pattern disturbances evoked by glutamate injection into the pedunculopontine tegmentum of anesthetized rats: Sleep: Journal of Sleep and Sleep Disorders Research Vol 28(5) Aug 2005, 560-570.
- Sarti, F., Borgland, S. L., Kharazia, V. N., & Bonci, A. (2007). Acute cocaine exposure alters spine density and long-term potentiation in the ventral tegmental area: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 26(3) Aug 2007, 749-756.
- Satorra-Marin, N., Coll-Andreu, M., Portell-Cortes, I., Aldavert-Vera, L., & Morgado-Bernal, I. (2001). Impairment of two-way active avoidance after pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus lesions: Effects of conditioned stimulus duration: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 118(1) Jan 2001, 1-9.
- Satorra-Marin, N., Homs-Ormo, S., Arevalo-Garcia, R., Morgado-Bernal, I., & Coll-Andreu, M. (2006). Erratum to "Effects of pre-training pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus lesions on delayed matching- and non-matching-to-position in a T-maze in rats": Behavioural Brain Research Vol 167(2) Feb 2006, 383.
- Sbarbati, A., Bunnemann, B., Cristofori, P., Terron, A., Chiamulera, C., Merigo, F., et al. (2002). Chronic nicotine treatment changes the axonal distribution of 68 kDa neurofilaments in the rat ventral tegmental area: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 16(5) Sep 2002, 877-882.
- Schenk, S., & Partridge, B. (1997). Effects of acute and repeated administration of N -methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) into the ventral tegmental area: Locomotor activating effects of NMDA and cocaine: Brain Research Vol 769(2) Sep 1997, 225-232.
- Schiff, B. B. (1964). The effects of tegmental lesions on the reward properties of septal stimulation: Psychonomic Science Vol 1(12) 1964, 397-398.
- Schilstrom, B., Rawal, N., Mameli-Engvall, M., Nomikos, G. G., & Svensson, T. H. (2003). Dual effects of nicotine on dopamine neurons mediated by different nicotinic receptor subtypes: International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 6(1) Mar 2003, 1-11.
- Schilstrom, B., Yaka, R., Argilli, E., Suvarna, N., Schumann, J., Chen, B. T., et al. (2006). Cocaine Enhances NMDA Receptor-Mediated Currents in Ventral Tegmental Area Cells via Dopamine D-sub-5 Receptor-Dependent Redistribution of NMDA Receptors: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 26(33) Aug 2006, 8549-8558.
- Schilstrom, B., Yaka, R., Argilli, E., Suvarna, N., Schumann, J., Chen, B. T., et al. (2006). "Cocaine Enhances NMDA Receptor-Mediated Currents in Ventral Tegmental Area Cells via Dopamine D-sub-5 Receptor-Dependent Redistribution of NMDA Receptors": Erratum: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 26(37) Sep 2006, 9604.
- Schott, B. H., Sellner, D. B., Lauer, C.-J., Habib, R., Frey, J. U., Guderian, S., et al. (2004). Activation of Midbrain Structures by Associative Novelty and the Formation of Explicit Memory in Humans: Learning & Memory Vol 11(4) Jul-Aug 2004, 383-387.
- Schramm-Sapyta, N. L., Olsen, C. M., & Winder, D. G. (2006). Cocaine Self-Administration Reduces Excitatory Responses in the Mouse Nucleus Accumbens Shell: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 31(7) Jul 2006, 1444-1451.
- Schubotz, R. I., & von Cramon, D. Y. (2004). Sequences of Abstract Nonbiological Stimuli Share Ventral Premotor Cortex with Action Observation and Imagery: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 24(24) Jun 2004, 5467-5474.
- Self, D. W., & Stein, L. (1993). Pertussis toxin attenuates intracranial morphine self-administration: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 46(3) Nov 1993, 689-695.
- Selken, J., & Nichols, D. E. (2007). alpha 1-Adrenergic receptors mediate the locomotor response to systemic administration of ()-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) in rats: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 86(4) Apr 2007, 622-630.
- Sesack, S. R., Carr, D. B., Omelchenko, N., & Pinto, A. (2003). Anatomical Substrates for Glutamate-Dopamine Interactions: Evidence for Specificity of Connections and Extrasynaptic Actions. New York, NY: New York Academy of Sciences.
- Sesack, S. R., & Pickel, V. M. (1995). Ultrastructural relationships between terminals immunoreactive for enkephalin, GABA, or both transmitters in the rat ventral tegmental area: Brain Research Vol 672(1-2) Feb 1995, 261-275.
- Shank, E. J., Seitz, P. K., Bubar, M. J., Stutz, S. J., & Cunningham, K. A. (2007). Selective ablation of GABA neurons in the ventral tegmental area increases spontaneous locomotor activity: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 121(6) Dec 2007, 1224-1233.
- Sharf, R. (2006). The role of acetylcholine neurotransmission in the ventral tegmental area on food reward and food-related learning. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Sharf, R., McKelvey, J., & Ranaldi, R. (2006). Blockade of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the ventral tegmental area prevents acquisition of food-rewarded operant responding in rats: Psychopharmacology Vol 186(1) May 2006, 113-121.
- Sharf, R., & Ranaldi, R. (2006). Blockade of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the ventral tegmental area disrupts food-related learning in rats: Psychopharmacology Vol 184(1) Jan 2006, 87-94.
- Sharp, P. E., Tinkelman, A., & Cho, J. (2001). Angular velocity and head direction signals recorded from the dorsal tegmental nucleus of gudden in the rat: Implications for path integration in the head direction cell circuit: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 115(3) Jun 2001, 571-588.
- Shen, R.-Y. (2003). Ethanol Withdrawal Reduces the Number of Spontaneously Active Ventral Tegmental Area Dopamine Neurons in Conscious Animals: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 307(2) Nov 2003, 566-572.
- Shen, R.-Y., Choong, K.-C., & Thompson, A. C. (2007). Long-Term Reduction in Ventral Tegmental Area Dopamine Neuron Population Activity Following Repeated Stimulant or Ethanol Treatment: Biological Psychiatry Vol 61(1) Jan 2007, 93-100.
- Shi, W.-X., Pun, C.-L., & Zhou, Y. (2004). Psychostimulants Induce Low-Frequency Oscillations in the Firing Activity of Dopamine Neurons: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 29(12) Dec 2004, 2160-2167.
- Shim, S. S., Bunney, B. S., & Shi, W.-X. (1996). Effects of lesions in the medial prefrontal cortex on the activity of midbrain dopamine neurons: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 15(5) Nov 1996, 437-441.
- Shimura, T., Kamada, Y., & Yamamoto, T. (2002). Ventral tegmental lesions reduce overconsumption of normally preferred taste fluid in rats: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 134(1-2) Aug 2002, 123-130.
- Shimura, T., & Shimokochi, M. (1990). Involvement of the lateral mesencephalic tegmentum in copulatory behavior of male rats: Neuron activity in freely moving animals: Neuroscience Research Vol 9(3) Dec 1990, 173-183.
- Shimura, T., & Shimokochi, M. (1991). Modification of male rat copulatory behavior by lateral midbrain stimulation: Physiology & Behavior Vol 50(5) Nov 1991, 989-994.
- Shippenberg, T. S., Bals-Kubik, R., Huber, A., & Herz, A. (1991). Neuroanatomical substrates mediating the aversive effects of D-1 dopamine receptor antagonists: Psychopharmacology Vol 103(2) Feb 1991, 209-214.
- Shippenburg, T. S., & Bals-Kubik, R. (1995). Involvement of the mesolimbic dopamine system in mediating the aversive effects of opioid antagonists in the rat: Behavioural Pharmacology Vol 6(2) Mar 1995, 99-106.
- Shumake, J., Edwards, E., & Gonzalez-Lima, F. (2003). Opposite metabolic changes in the habenula and ventral tegmental area of a genetic model of helpless behavior: Brain Research Vol 963(1-2) Feb 2003, 274-281.
- Simmons, D. A., Brooks, B. M., & Neill, D. B. (2007). GABAergic inactivation of basolateral amygdala alters behavioral processes other than primary reward of ventral tegmental self-stimulation: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 181(1) Jul 2007, 110-117.
- Simpson, J. I., Leonard, C. S., & Soodak, R. E. (1988). The accessory optic system: Analyzer of self-motion: Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences Vol 545 Dec 1988, 170-179.
- Singh, J., Desiraju, T., & Raju, T. R. (1996). Comparison of intracranial self-stimulation evoked from lateral hypothalamus and ventral tegmentum: Analysis based on stimulation parameters and behavioural response characteristics: Brain Research Bulletin Vol 41(6) 1996, 399-408.
- Singh, J., Desiraju, T., & Raju, T. R. (1997). Dopamine receptor sub-types involvement in nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmentum but not in medial prefrontal cortex: On self-stimulation of lateral hypothalamus and ventral mesencephalon: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 86(2) Jul 1997, 171-179.
- Sipos, M. L., & Nyby, J. G. (1996). Concurrent androgenic stimulation of the ventral tegmental area and medial preoptic area: Synergistic effects on male-typical reproductive behaviors in house mice: Brain Research Vol 729(1) Aug 1996, 29-44.
- Smeraski, C. A. (1998). Electrophysiology of the ventral midbrain in the frog, rana pipiens: A stimulation and recording study of the tecto-tegmental projection and tecto-isthmotectal projection. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Smotherman, M., Zhang, S., & Metzner, W. (2003). A neural basis for auditory feedback control of vocal pitch: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 23(4) Feb 2003, 1464-1477.
- Song, P., & Wang, X.-J. (2005). Angular Path Integration by Moving "Hill of Activity": A Spiking Neuron Model without Recurrent Excitation of the Head-Direction System: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 25(4) Jan 2005, 1002-1014.
- Sotres-Bayon, F., Torres-Lopez, E., Lopez-Avila, A., del Angel, R., & Pellicar, F. (2001). Lesion and electrical stimulation of the ventral tegmental area modify persistent nociceptive behavior in the rat: Brain Research Vol 898(2) Apr 2001, 342-349.
- Steckler, T., Inglis, W., Winn, P., & Sahgal, A. (1994). The pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus: A role in cognitive processes? : Brain Research Reviews Vol 19(3) Aug 1994, 298-318.
- Steckler, T., Keith, A. B., & Sahgal, A. (1994). Lesions of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus do not alter delayed non-matching to position accuracy: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 61(1) Mar 1994, 107-112.
- Steffensen, S. C., Lee, R.-S., Stobbs, S. H., & Henriksen, S. J. (2001). Responses of ventral tegmental area GABA neurons to brain stimulation reward: Brain Research Vol 906(1-2) Jul 2001, 190-197.
- Steffensen, S. C., Svingos, A. L., Pickel, V. M., & Henriksen, S. J. (1998). Electrophysiological characterization of GABAergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 18(19) Oct 1998, 8003-8015.
- Steiniger, B., & Kretschmer, B. D. (2004). Effects of ibotenate pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus lesions on exploratory behaviour in the open field: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 151(1-2) May 2004, 17-23.
- Steketee, J. D. (1994). Intra-A10 injection of H7 blocks the development of sensitization to cocaine: Neuroreport: An International Journal for the Rapid Communication of Research in Neuroscience Vol 6(1) Dec 1994, 69-72.
- Steketee, J. D. (1997). Intra-ventral tegmental area administration of H7 delays, but does not prevent the development of cocaine-induced sensitization: Brain Research Bulletin Vol 43(6) 1997, 565-571.
- Steketee, J. D. (1998). Injection of SCH 23390 into the ventral tegmental area blocks the development of neurochemical but not behavioural sensitization to cocaine: Behavioural Pharmacology Vol 9(1) Feb 1998, 69-76.
- Steketee, J. D. (1998). Repeated injection of GBR 12909, but not cocaine or WIN 35,065-2, into the ventral tegmental area induces behavioral sensitization: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 97(1-2) Dec 1998, 39-48.
- Stoessl, A. J., Polanski, E., & Frydryszak, H. (1993). Effects of ageing on tachykinin function in the basal ganglia: Brain Research Vol 632(1-2) Dec 1993, 21-28.
- Struthers, W. M. (2001). Sex-induced fos in the medial preoptic area: Projections to the midbrain: Neuroreport: For Rapid Communication of Neuroscience Research Vol 12(14) Oct 2001, 3065-3068.
- Subramaniam, S., Marcotte, E. R., & Srivastava, L. K. (2001). Differential changes in synaptic terminal protein expression between nucleus accumbens core and shell in the amphetamine-sensitized rat: Brain Research Vol 901(1-2) May 2001, 175-183.
- Sumida, K., Walf, A. A., & Frye, C. A. (2005). Progestin-facilitated lordosis of hamsters may involve dopamine-like type 1 receptors in the ventral tegmental area: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 161(1) Jun 2005, 1-7.
- Sun, W., Akins, C. K., Mattingly, A. E., & Rebec, G. V. (2005). Lonotropic glutamate receptors in the ventral tegmental area regulate cocaine-seeking behavior in rats: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 30(11) Nov 2005, 2073-2081.
- Surkis, A. (1997). Quantitative analysis of morphology and membrane properties of laterodorsal tegmental neurons. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering.
- Suto, N., Austin, J. D., Tanabe, L. M., Kramer, M. K., Wright, D. A., & Vezina, P. (2002). Previous exposure to VTA amphetamine enhances cocaine self-administration under a progressive ratio schedule in a D-sub-1 dopamine receptor dependent manner: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 27(6) Dec 2002, 970-979.
- Suto, N., Tanabe, L. M., Austin, J. D., Creekmore, E., & Vezina, P. (2003). Previous exposure to VTA amphetamine enhances cocaine self-administration under a progressive ratio schedule in an NMDA, AMPA/kainate, and metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent manner: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 28(4) Apr 2003, 629-639.
- Swanson, C. J., & Kalivas, P. W. (2000). Regulation of locomotor activity by metabotropic glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmental area: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 292(1) Jan 2000, 406-414.
- Sweet, D. C., Levine, A. S., Billington, C. J., & Kotz, C. M. (1999). Feeding response to central orexins: Brain Research Vol 821(2) Mar 1999, 535-538.
- Swerdlow, N. R., & Geyer, M. A. (1993). Prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle in rats after lesions of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus: Behavioral Neuroscience Vol 107(1) Feb 1993, 104-117.
- Szabo, B., Siemes, S., & Wallmichrath, I. (2002). Inhibition of GABAergic neurotransmission in the ventral tegmental area by cannabinoids: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 15(12) Jun 2002, 2057-2061.
- Takahashi, K., Koyama, Y., Kayama, Y., & Yamamoto, M. (2002). Effects of orexin on the laterodorsal tegmental neurones: Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences Vol 56(3) Jun 2002, 335-336.
- Takahashi, K., Nagai, T., Kamei, H., Maeda, K., Matsuya, T., Arai, S., et al. (2007). Neural circuits containing pallidotegmental GABAergic neurons are involved in the prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex in mice: Biological Psychiatry Vol 62(2) Jul 2007, 148-157.
- Takakusaki, K. (2008). Forebrain control of locomotor behaviors: Brain Research Reviews Vol 57(1) Jan 2008, 192-198.
- Takakusaki, K., Saitoh, K., Harada, H., & Kashiwayanagi, M. (2004). Role of basal ganglia-brainstem pathways in the control of motor behaviors: Neuroscience Research Vol 50(2) Oct 2004, 137-151.
- Tammer, R., Ehrenreich, L., & Jurgens, U. (2004). Telemetrically recorded neuronal activity in the inferior colliculus and bordering tegmentum during vocal communication in squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus): Behavioural Brain Research Vol 151(1-2) May 2004, 331-336.
- Tanabe, L. M., Suto, N., Creekmore, E., Steinmiller, C. L., & Vezina, P. (2004). Blockade of D-sub-2 dopamine receptors in the VTA induces a long-lasting enhancement of the locomotor activating effects of amphetamine: Behavioural Pharmacology Vol 15(5-6) Sep 2004, 387-395.
- Tao, L., & Ye, J. H. (2002). Protein kinase C modulation of ethanol inhibition of glycine-activated current in dissociated neurons of rat ventral tegmental area: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 300(3) Mar 2002, 967-975.
- Taylor, C. L., Kozak, R., Latimer, M. P., & Winn, P. (2004). Effects of changing reward on performance of the delayed spatial win-shift radial maze task in pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus lesioned rats: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 153(2) Aug 2004, 431-438.
- Thompson, A. C. (1993). The effect of altered opioid activity in the ventral tegmental area on the onset of maternal behavior in the rat: Dissertation Abstracts International.
- Thompson, A. C., & Kristal, M. B. (1996). Opioid stimulation in the ventral tegmental area facilitates the onset of maternal behavior in rats: Brain Research Vol 743(1-2) Dec 1996, 184-201.
- Thompson, R. (1958). The effect of intracranial stimulation on memory in cats: Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology Vol 51(4) Aug 1958, 421-426.
- Todorova, A., & Dimpfel, W. (1994). Multiunit activity from the A9 and A10 areas in rats following chronic treatment with different neuroleptic drugs: European Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 4(4) Dec 1994, 491-501.
- Tolliver, B. K., Ho, L. B., Fox, L. M., & Berger, S. P. (1999). Necessary role for ventral tegmental area adenylate cyclase and protein kinase A in induction of behavioral sensitization to intraventral tegmental area amphetamine: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 289(1) Apr 1999, 38-47.
- Tolliver, B. K., Ho, L. B., Reid, M. S., & Berger, S. P. (1996). Evidence for involvement of ventral tegmental area cyclic AMP systems in behavioral sensitization to psychostimulants: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 278(1) Jul 1996, 411-420.
- Tran-Nguyen, L. T. L., Castaneda, E., & MacBeth, T. (1996). Changes in behavior and monoamine levels in microdialysate from dorsal striatum after 6-OHDA infusions into ventral striatum: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 55(1) Sep 1996, 141-150.
- Trojniar, W., & Klejbor, I. (1999). Facilitatory effect of unilateral lesion of the ventral tegmental area on locomotor reponse to stimulation of the contralateral ventral tegmental area: Involvement of GABAergic transmission: Brain Research Vol 842(2) Sep 1999, 419-430.
- Trojniar, W., & Staszewska, M. (1994). Unilateral damage to the ventral tegmental area facilitates feeding induced by stimulation of the contralateral ventral tegmental area: Brain Research Vol 641(2) Apr 1994, 333-340.
- Trojniar, W., & Staszewska, M. (1995). Bilateral lesions of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus affect feeding induced by electrical stimulation of the ventral tegmental area: Acta Neurobiologiae Experimentalis Vol 55(3) 1995, 201-206.
- Tsibulsky, V. L., Grocki, S., Dashevsky, B. A., Kehne, J. H., Schmidt, C. J., Sorensen, S. M., et al. (1998). Mixed D-sub-2/5-HT-sub(2A ) antagonism of cocaine-induced facilitation of brain stimulation reward: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 59(2) Feb 1998, 275-280.
- Tu, Y., Kroener, S., Abernathy, K., Lapish, C., Seamans, J., Chandler, L. J., et al. (2007). Ethanol inhibits persistent activity in prefrontal cortical neurons: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 27(17) Apr 2007, 4765-4775.
- Tuomainen, P., Patsenka, A., Hyytia, P., Grinevich, V., & Kiianmaa, K. (2003). Extracellular levels of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens in AA and ANA rats after reverse microdialysis of ethanol into the nucleus accumbens or ventral tegmental area: Alcohol Vol 29(2) Feb 2003, 117-124.
- Tzschentke, T. M., & Schmidt, W. J. (2000). Functional relationship among medial prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, and ventral tegmental area in locomotion and reward: Critical Reviews in Neurobiology Vol 14(2) 2000, 131-142.
- Uemura, K., & Preston, J. B. (1965). Comparison of motor cortex influences upon various hind-limb motoneurons in pyramidal cats and primates: Journal of Neurophysiology 28(2) 1965, 398-412.
- Ulloor, J., Mavanji, V., Saha, S., Siwek, D. F., & Datta, S. (2004). Spontaneous REM Sleep Is Modulated By the Activation of the Pedunculopontine Tegmental GABA-sub(B) Receptors in the Freely Moving Rat: Journal of Neurophysiology Vol 91(4) Apr 2004, 1822-1831.
- Ungless, M. A., Magill, P. J., & Bolam, J. P. (2004). Uniform Inhibition of Dopamine Neurons in the Ventral Tegmental Area by Aversive Stimuli: Science Vol 303(5666) Mar 2004, 2040-2042.
- Uramura, K., Funahashi, H., Muroya, S., Shioda, S., Takigawa, M., & Yada, T. (2001). Orexin-a activates phospholipase C- and protein kinase C-mediated Ca-super(2+ ) signaling in dopamine neurons of the ventral tegmental area: Neuroreport: For Rapid Communication of Neuroscience Research Vol 12(9) Jul 2001, 1885-1889.
- van Furth, W. R., & van Ree, J. M. (1996). Sexual motivation: Involvement of endogenous opioids in the ventral tegmental area: Brain Research Vol 729(1) Aug 1996, 20-28.
- Verca, M. S. B., Bahi, A., Boyer, F., Wagner, G. C., & Dreyer, J.-L. (2003). Distribution of alpha - and gamma -synucleins in the adult rat brain and their modification by high-dose cocaine treatment: European Journal of Neuroscience Vol 18(7) Oct 2003, 1923-1938.
- Vezina, P. (1996). D/1 dopamine activation is necessary for the induction of sensitization by amphetamine in the ventral tegmental area: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 16(7) Apr 1996, 2411-2420.
- Vezina, P., & Queen, A. L. (2000). Induction of locomotor sensitization by amphetamine requires the activation of NMDA receptors in the rat ventral tegmental area: Psychopharmacology Vol 151(2-3) Aug 2000, 184-191.
- Voneida, T. J. (1999). The effect of rubrospinal tractotomy on a conditioned limb response in the cat: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 105(2) Nov 1999, 151-162.
- Vos, P. E., Steinbusch, H. W. M., Ronken, E., & van Ree, J. M. (1999). Short and long term plasticity after lesioning of the cell body or terminal field area of the dopaminergic mesocorticolimbic system in the rat: Brain Research Vol 831(1-2) Jun 1999, 237-247.
- Walker, B. M., & Ettenberg, A. (2005). Intra-ventral tegmental area heroin-induced place preferences in rats are potentiated by peripherally administered alprazolam: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 82(3) Nov 2005, 470-477.
- Wang, B., Luo, F., Ge, X.-C., Fu, A.-H., & Han, J.-S. (2002). Effects of lesions of various brain areas on drug priming or footshock-induced reactivation of extinguished conditioned place preference: Brain Research Vol 950(1-2) Sep 2002, 1-9.
- Wang, B., Shaham, Y., Zitzman, D., Azari, S., Wise, R. A., & You, Z.-B. (2005). Cocaine Experience Establishes Control of Midbrain Glutamate and Dopamine by Corticotropin-Releasing Factor: A Role in Stress-Induced Relapse to Drug Seeking: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 25(22) Jun 2005, 5389-5396.
- Wang, B., You, Z.-B., Rice, K. C., & Wise, R. A. (2007). Stress-induced relapse to cocaine seeking: Roles for the CRF-sub-2 receptor and CRF-binding protein in the ventral tegmental area of the rat: Psychopharmacology Vol 193(2) Aug 2007, 283-294.
- Wang, H.-D., Takigawa, M., Hamada, K., Shiratani, T., & Takenouchi, K. (2002). A shift in information flow between prefrontal cortex and the ventral tegmental area in methamphetamine-sensitized rats: International Journal of Psychophysiology Vol 44(3) Jun 2002, 250-259.
- Wang, H.-D., Takigawa, M., Hamada, K., Shiratani, T., Takenouchi, K., & Wang, G. (2000). Reciprocal information flow between prefrontal cortex and ventral tegmental area in an animal model of schizophrenia: Neuroreport: For Rapid Communication of Neuroscience Research Vol 11(9) Jun 2000, 2007-2011.
- Wang, H.-L., Zhao, Y., Xiang, X.-H., Wang, H.-S., & Wu, W.-R. (2004). Blockade of ionotropic glutamatergic transmission in the ventral tegmental area attenuates the physical signs of morphine withdrawal in rats: Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry Vol 28(7) Nov 2004, 1079-1087.
- Wang, T., & French, E. D. (1993). Effects of phencyclidine on spontaneous and excitatory amino acid-induced activity of ventral tegmental dopamine neurons: An extracellular in vitro study: Life Sciences Vol 53(1) 1993, 49-56.
- Waraczynski, M., & Shizgal, P. (1995). Self-stimulation of the MFB following parabrachial lesions: Physiology & Behavior Vol 58(3) Sep 1995, 559-566.
- Waraczynski, M., Ton, M. N., & Shizgal, P. (1990). Failure of amygdaloid lesions to increase the threshold for self-stimulation of the lateral hypothalamus and ventral tegmental area: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 40(2) Nov 1990, 159-168.
- Watanabe, T., Morimoto, K., Nakamura, M., & Suwaki, H. (1998). Modification of behavioral responses induced by electrical stimulation of the ventral tegmental area in rats: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 93(1-2) Jun 1998, 119-129.
- Weinstein, D. M., Narayanan, S., Byrnes, J. J., Uretsky, N. J., & Wallace, L. J. (1997). Comparison of sensitization elicited by amphetamine and pertussis toxin: Characterization of locomotor behavior and limbic dopamine release: Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry Vol 21(5) Jul 1997, 885-897.
- Whishaw, I. Q., & Gorny, B. (1996). Does the red nucleus provide the tonic support against which fractionated movements occur? A study on forepaw movements used in skilled reaching by the rat: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 74(1-2) Jan 1996, 79-90.
- White, F. J. (1996). Synaptic regulation of mesocorticolimbic dopamine neurons: Annual Review of Neuroscience Vol 19 1996, 405-436.
- Whyte, D. G., Brennan, T. J., & Johnson, A. K. (2006). Thermoregulatory behavior is disrupted in rats with lesions of the anteroventral third ventricular area (AV3V): Physiology & Behavior Vol 87(3) Mar 2006, 493-499.
- Williams, J. A., & Reiner, P. B. (1993). Noradrenaline hyperpolarizes identified rat mesopontine cholinergic neurons in vitro: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 13(9) Sep 1993, 3878-3883.
- Willins, D. L. (1993). The role of excitatory amino acid receptors in the basal forebrain in the locomotor response produced by psychostimulants and the non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist MK801: Dissertation Abstracts International.
- Wolf, M. E., White, F. J., & Hu, X.-T. (1994). MK-801 prevents alterations in the mesoaccumbens dopamine system associated with behavioral sensitization to amphetamine: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 14(3, Pt 2) Mar 1994, 1735-1745.
- Wolske, M., Rompre, P. P., Wise, R. A., & West, M. O. (1993). Activation of single neurons in the rat nucleus accumbens during self-stimulation of the ventral tegmental area: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 13(1) Jan 1993, 1-12.
- Wu, X., & French, E. D. (2000). Effects of chronic Delta -sup-9-tetrahydrocannabinol on rat midbrain dopamine neurons: An electrophysiological assessment: Neuropharmacology Vol 39(3) 2000, 391-398.
- Xi, M.-C., Morales, F. R., & Chase, M. H. (2001). Effects on sleep and wakefulness of the injection of hypocretin-1 (orexin-A) into the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus of the cat: Brain Research Vol 901(1-2) May 2001, 259-264.
- Xi, Z.-X., & Stein, E. (2002). Blockade of ionotropic glutamatergic transmission in the ventral tegmental area reduces heroin reinforcement in rat: Psychopharmacology Vol 164(2) Nov 2002, 144-150.
- Xi, Z.-X., & Stein, E. A. (2002). GABAergic mechanisms of opiate reinforcement: Alcohol and Alcoholism Vol 37(5) Sep-Oct 2002, 485-494.
- Xie, J.-X., Tang, M., & Zhang, C. (2001). Effect of cholecystokinin-8 microinjection into ventral tegmental area on dopamine release in nucleus accumbens of rats: An in vivo voltammetric study: Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry Vol 25(2) Feb 2001, 427-434.
- Xu, C., & Shen, R.-Y. (2001). Amphetamine normalizes the electrical activity of dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area following prenatal ethanol exposure: Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Vol 297(2) May 2001, 746-752.
- Yamanouchi, K., Nakano, Y., & Arai, Y. (1990). Roles of the pontine dorsomedial tegmentum and midbrain central gray in regulating female rat sexual behaviors: Effects of p-chlorophenylalanine: Brain Research Bulletin Vol 25(3) Sep 1990, 381-385.
- Yamazaki, Y., Ishioka, M., Matsubayashi, H., Amano, T., & Sasa, M. (2002). Inhibition by sigma receptor ligand, MS-377, of N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced currents in dopamine neurons of the rat ventral tegmental area: Psychopharmacology Vol 161(1) Apr 2002, 64-69.
- Yan, Q.-S., Zheng, S.-Z., Feng, M.-J., & Yan, S.-E. (2005). Involvement of 5-HT-sub(1B) receptors within the ventral tegmental area in ethanol-induced increases in mesolimbic dopaminergic transmission: Brain Research Vol 1060(1-2) Oct 2005, 126-137.
- Yang, P. B., Swann, A. C., & Dafny, N. (2006). Chronic methylphenidate modulates locomotor activity and sensory evoked responses in the VTA and NAc of freely behaving rats: Neuropharmacology Vol 51(3) Sep 2006, 546-556.
- Yang, P. B., Swann, A. C., & Dafny, N. (2006). Sensory-evoked potentials recordings from the ventral tegmental area, nucleus accumbens, prefrontal cortex, and caudate nucleus and locomotor activity are modulated in dose-response characteristics by methylphenidate: Brain Research Vol 1073-1074 Feb 2006, 164-174.
- Ye, J. H., Tao, L., Zhu, L., Krnjevic, K., & McArdle, J. J. (2001). Ethanol inhibition of glycine-activated responses in neurons of ventral tegmental area of neonatal rats: Journal of Neurophysiology Vol 86(5) Nov 2001, 2426-2434.
- Yeomans, J., & Baptista, M. (1997). Both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors in ventral tegmental area contribute to brain-stimulation reward: Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior Vol 57(4) Aug 1997, 915-921.
- Yeomans, J. S. (1995). Role of tegmental cholinergic neurons in dopaminergic activation, antimuscarinic psychosis and schizophrenia: Neuropsychopharmacology Vol 12(1) Feb 1995, 3-16.
- Yeomans, J. S., Takeuchi, J., Baptista, M., Flynn, D. D., Lepik, K., Nobrega, J., et al. (2000). Brain-stimulation reward thresholds raised by an antisense oligonucleotide for the M5 muscarinic receptor infused near dopamine cells: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 20(23) Dec 2000, 8861-8867.
- Yun, I. A., Wakabayashi, K. T., Fields, H. L., & Nicola, S. M. (2004). The Ventral Tegmental Area is Required for the Behavioral and Nucleus Accumbens Neuronal Firing Responses to Incentive Cues: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 24(12) Mar 2004, 2923-2933.
- Zacharko, R. M., Maddeaux, C., Hebb, A. L. O., Mendella, P. D., & Marsh, N. J. (1998). Vulnerability to stressor-induced disturbances in self-stimulation from the dorsal and ventral A10 area: Differential effects of intraventricular D-Alasuperscript 2-Met-sup-5-enkephalinamide, D-Alasuperscript 2, N-Me-Phe-sup-4, Gly-Ol-sup-5-enkaphalin, and D-Pensuperscript 2, D-Pen-sup-5-enkephalin administration: Brain Research Bulletin Vol 47(3) Oct 1998, 237-248.
- Zangen, A., Ikemoto, S., Zadina, J. E., & Wise, R. A. (2002). Rewarding and Psychomotor Stimulant Effects of Endomorphin-1: Anteroposterior Differences within the Ventral Tegmental Area and Lack of Effect in Nucleus Accumbens: Journal of Neuroscience Vol 22(16) Aug 2002, 7225-7233.
- Zarrindast, M.-R., Farajzadeh, Z., Rostami, P., Rezayof, A., & Nourjah, P. (2005). Involvement of the ventral tegmental area (VTA) in morphine-induced memory retention in morphine-sensitized rats: Behavioural Brain Research Vol 163(1) Aug 2005, 100-106.
- Zhang, H., Kiyatkin, E. A., & Stein, E. A. (1994). Behavioral and pharmacological modulation of ventral tegmental dendritic dopamine release: Brain Research Vol 656(1) Sep 1994, 59-70.
- Zhang, J., Engel, J. A., Hjorth, S., & Svensson, L. (1995). Changes in the acoustic startle response and prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle in rats after local injection of pertussis toxin into the ventral tegmental area: Psychopharmacology Vol 119(1) May 1995, 71-78.
- Zhu, L., Jiang, Z. L., Krnjevic, K., Wang, F. S., & Ye, J. H. (2003). Genistein directly blocks glycine receptors of rat neurons freshly isolated from the ventral tegmental area: Neuropharmacology Vol 45(2) Aug 2003, 270-280.
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |