No edit summary |
|||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
* [[X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia|X-linked agammaglobulinemia]] |
* [[X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia|X-linked agammaglobulinemia]] |
||
* [[X-linked ichthyosis]] |
* [[X-linked ichthyosis]] |
||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Sex-linked traits in other mammals == |
== Sex-linked traits in other mammals == |
||
| Line 37: | Line 39: | ||
[[sr:Наслеђивање везано за X хромозом]] |
[[sr:Наслеђивање везано за X хромозом]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{enWP|Sex linkage}} |
{{enWP|Sex linkage}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Latest revision as of 15:44, 12 November 2010
Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
Sex linkage is the phenotypic expression of an allele that is dependent on the sex of the individual and is directly tied to the sex chromosomes.
In such cases there is a homogametic sex and a heterogametic sex. In mammals the homogametic sex is female (XX) and the heterogametic sex is male (XY), thus the sex linked genes are carried on the X chromosome. In birds and some insects the homogametic sex is male and has ZZ chromosomes, with females ZW, sex-linked genes are on the Z chromosome, and "male" and "female" are exchanged.
Dominant sex-linked genes are rare. Potentially expressed in both sexes, a sex preference may still exist.
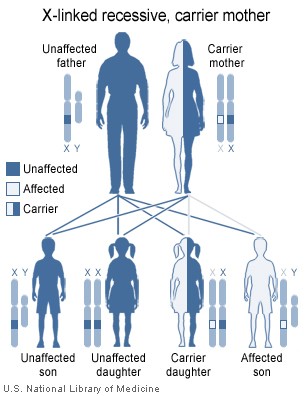
X-linked recessive genes are expressed in all heterogametics, but only those homogametics that are homozygous for the recessive allele. An example is the sex-linked recessive: horns in sheep that appear only in males. The recessive phenotypes of such genes are more common in males than in females; to be precise, the incidence in females is the square of that in males, so if 1/20 of the male population is green-blind, 1/400 of the female population is. (AIS does not follow this rule because it interferes with reproduction.)
Sex-linked traits are inherited through chains of carrier mothers. That is, a girl, her mother, and her mother's mother all are carriers, while some of their sons have the trait.
Sex-linked traits in humans
X-linked dominant
X-linked recessive
- Adrenoleukodystrophy
- Androgen insensitivity syndrome
- Barth syndrome
- Becker's muscular dystrophy
- Color blindness: Red and green
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Fragile X syndrome
- G6PD deficiency
- Hemophilia
- Kennedy disease
- Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
- Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency
- Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- X-linked agammaglobulinemia
- X-linked ichthyosis
Sex-linked traits in other mammals
- cats: Orange and black fur
sr:Наслеђивање везано за X хромозом
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |