Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
| Nerve: Radial nerve | ||
|---|---|---|
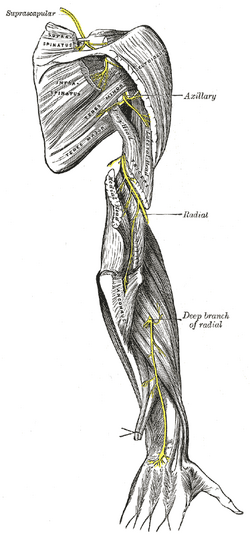
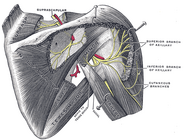
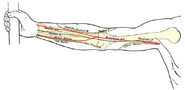
| The suprascapular, axillary, and radial nerves. | ||
| [[Image:|250px|center|]] | ||
| Latin | nervus radialis | |
| Gray's | subject #210 943 | |
| Innervates | posterior compartment of the arm, posterior compartment of the forearm | |
| From | posterior cord | |
| To | posterior interosseous nerve | |
| MeSH | A08.800.800.720.050.700 | |
- Main article: Spinal nerves
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the arm, the forearm and the hand.
It originates from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus with roots from C5, 6, 7, 8, & T1.
The radial nerve and its branches supply the dorsal muscles, such as triceps brachii, the extrinsic extensors of the wrist and hands, and the cutaneous nerve supply to most of the back of the hand. (The ulnar nerve cutaneously innervates the back of the little finger.)
The radial nerve divides into a deep branch, (which becomes the posterior interosseous nerve), and continues as the superficial branch which goes on to innervate the dorsum (back) of the hand.
Course[]
The radial nerve originates as a terminal branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus.
Posterior[]
From the brachial plexus, it travels posteriorly through what often called the triangular interval.
The radial nerve enters the arm behind the axillary artery/brachial artery, and it then travels posteriorly on the medial side of the arm.
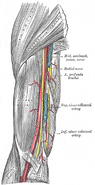
After giving off branches to the long and lateral heads of the triceps brachii, it enters a groove on the humerus, the radial sulcus.
Along with the deep brachial artery, the radial nerve winds around in the groove (between the medial and lateral heads of the triceps) towards the forearm, running laterally on the posterior aspect of the humerus.
While in the groove, it gives off a branch to the medial head of the triceps brachii.
The radial nerve emerges from the groove on the lateral aspect of the humerus.
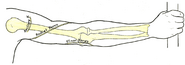
Anterior[]
At this point, it pierces the lateral intermuscular septum and enters the anterior compartment of the arm.
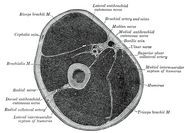
It continues its journey inferiorly between the brachialis and brachioradialis muscles.
When the radial nerve reaches the distal part of the humerus, it passes in front of the lateral epicondyle.
It then branches into a superficial branch (primarily sensory) and a deep branch (primarily motor).
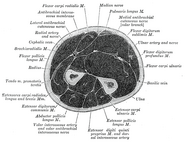
- The superficial branch of the radial nerve descends in the forearm under the brachioradialis. It eventually pierces the deep fascia near the back of the wrist.
- The deep branch of the radial nerve pierces the supinator muscle, after which it is known as the posterior interosseous nerve.
Branches/Innervations[]
The following are branches/innervations of the radial nerve (including the superficial branch of the radial nerve and the deep branch of the radial nerve/posterior interosseous nerve).
Cutaneous[]
Cutaneous innervation is provided by the following nerves:
- Posterior cutaneous nerve of arm (originates in axilla)
- Inferior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm (originates in arm)
- Posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm (originates in arm)
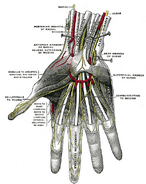
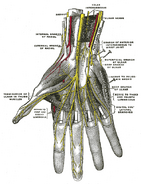
The superficial branch of the radial nerve provides sensory innervation to much of the back of the hand, including the web of skin between the thumb and index finger.
Motor[]
Muscular branches of the radial nerve:
- Triceps brachii
- Anconeus
- Brachioradialis
- Extensor carpi radialis longus
Deep branch of the radial nerve:
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis
- Supinator
Posterior interosseous nerve (a continuation of the deep branch after the supinator):
- Extensor digitorum
- Extensor digiti minimi
- Extensor carpi ulnaris
- Abductor pollicis longus
- Extensor pollicis brevis
- Extensor pollicis longus
- Extensor indicis
The radial nerve (and its deep branch) provides motor innervation to the muscles in the posterior compartment of the arm and forearm, which are mostly extensors.
Additional images[]
See also[]
- Muscular branches of the radial nerve
- Cutaneous branches of the radial nerve
- Superficial branch of the radial nerve
- Deep branch of the radial nerve
External links[]
- Duke Orthopedics radial_nerve
- Atlas of anatomy at UMich hand_plexus - "Axilla, dissection, anterior view"
| Nerves of upper limbs (primarily): the brachial plexus |
|---|
| supraclavicular: dorsal scapular - suprascapular - to the subclavius - long thoracic
infraclavicular: lateral cord: musculocutaneous (lateral cutaneous of forearm) - lateral pectoral - lateral head of median (anterior interosseous, palmar, common palmar digital, proper palmar digital) medial cord: medial pectoral - medial cutaneous of forearm - medial cutaneous of arm - ulnar (muscular branches, dorsal branch, palmar branch, superficial branch, deep branch) - medial head of median posterior cord: subscapular (upper, lower) - thoracodorsal - axillary (superior lateral cutaneous of arm) - radial (muscular, inferior lateral cutaneous of arm, posterior cutaneous of arm, posterior cutaneous of forearm, superficial branch, deep branch, posterior interosseous) |
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |
{{en