Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
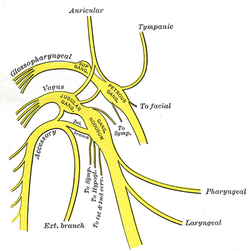
| Nerve: Pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve | ||
|---|---|---|
| Plan of upper portions of glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves. (Pharyngeal visible at center right.) | ||
| [[Image:|250px|center|]] | ||
| Latin | ramus pharyngeus nervi vagi | |
| Gray's | subject #205 911 | |
| Innervates | ||
| From | vagus nerve | |
| To | ||
| MeSH | [1] | |
The pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve, the principal motor nerve of the pharynx, arises from the upper part of the ganglion nodosum, and consists principally of filaments from the cranial portion of the accessory nerve.
It passes across the internal carotid artery to the upper border of the Constrictor pharyngis medius, where it divides into numerous filaments, which join with branches from the glossopharyngeal, sympathetic, and external laryngeal to form the pharyngeal plexus.
From the plexus, branches are distributed to the muscles and mucous membrane of the pharynx (except the the stylopharyngeus) and the muscles of the soft palate, except the Tensor veli palatini. A minute filament descends and joins the hypoglossal nerve as it winds around the occipital artery.
See also[]
External links[]
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained herein may be outdated. Please edit the article if this is the case, and feel free to remove this notice when it is no longer relevant.
I-IV: olfactory - optic - oculomotor - trochlear
V: trigeminal: trigeminal ganglion
V1: ophthalmic: lacrimal - frontal (supratrochlear, supraorbital) - nasociliary (long root of ciliary, long ciliary, infratrochlear, posterior ethmoidal, anterior ethmoidal) - ciliary ganglion (short ciliary)
V2: maxillary: middle meningeal - in the pterygopalatine fossa (zygomatic, zygomaticotemporal, zygomaticofacial, sphenopalatine, posterior superior alveolar)
in the infraorbital canal/infraorbital nerve (middle superior alveolar, anterior superior alveolar)
on the face (inferior palpebral, external nasal, superior labial, infraorbital plexus) - pterygopalatine ganglion (deep petrosal, nerve of pterygoid canal)
branches of distribution (palatine, nasopalatine, pharyngeal)
V3: mandibular: nervus spinosus - medial pterygoid - anterior (masseteric, deep temporal, buccal, lateral pterygoid)
posterior (auriculotemporal, lingual, inferior alveolar, mylohyoid, mental) - otic ganglion - submandibular ganglion
VI: abducens
VII: facial: nervus intermedius - geniculate - inside facial canal (greater petrosal, nerve to the stapedius, chorda tympani)
at exit from stylomastoid foramen (posterior auricular, digastric - stylohyoid)
on face (temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, cervical)
VIII: vestibulocochlear: cochlear (striae medullares, lateral lemniscus) - vestibular
IX: glossopharyngeal: fasciculus solitarius - nucleus ambiguus - ganglia (superior, petrous) - tympanic - carotid sinus
X: vagus: ganglia (jugular, nodose) - Alderman's nerve - in the neck (pharyngeal branch, superior laryngeal ext and int, recurrent laryngeal)
in the thorax (pulmonary branches, esophageal plexus) - in the abdomen (gastric plexuses, celiac plexus, gastric plexus)
XI: accessory XII: hypoglossal
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |