Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
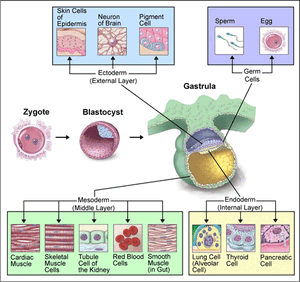
In animal development, organogenesis is the process by which the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm develop into the internal organs of the organism. The germ layers in organogenesis differ by three processes: folds, splits, and condensation. Developing early during this stage in chordate animals are the neural tube and notochord. Vertebrate animals all differ from the gastrula the same way. Vertebrates develop a neural crest that differentiates into many structures, including some bones, muscles, and components of the peripheral nervous system. The coelom of the body forms from a split of the mesoderm along the somite axis.
Production[]
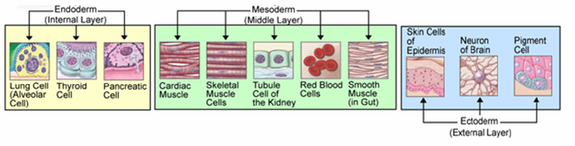
The endoderm produces tissue within the lungs, thyroid, and pancreas. The mesoderm aids in the production of cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, tissues within the kidneys, and red blood cells. The ectoderm produces tissues within the epidermis and aids in the formation of neurons within the brain, and melanocytes.
Organs derived from each germ layer. Image from NCBI.
The proceeding graph represents the products produced by the three germ layers.
| Germ Layer | Category | Product |
|---|---|---|
| Endoderm | General[1] | Gastrointestinal tract |
| Endodern | General | Respiratory tract |
| Endoderm | General | Endocrine glands and organs (liver and pancreas) |
| Mesoderm | General | Bones |
| Mesoderm | General | Most of the Circulatory system |
| Mesoderm | General | Connective tissues of the gut and integuments |
| Mesoderm | General | Excretory Tract |
| Mesoderm | General | Mesenchyme |
| Mesoderm | General | Mesothelium |
| Mesoderm | General | Muscles |
| Mesoderm | General | Peritoneum |
| Mesoderm | General | Reproductive System |
| Mesoderm | General | Urinary System |
| Mesoderm | Vertebrate[2] | Chordamesoderm |
| Mesoderm | Vertebrate | Paraxial mesoderm |
| Mesoderm | Vertebrate | Intermediate mesoderm |
| Mesoderm | Vertebrate | Lateral plate mesoderm |
| Ectoderm | General | Nervous system |
| Ectoderm | General | Outer part of integument |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Skin (along with glands, hair, nails) |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Epithelium of the mouth and nasal cavity |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Lens and cornea of the eye |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Melanocytes |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Peripheral nervous system |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Facial cartilage |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Dentin (in teeth) |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Brain (rhombencephalon, mesencephalon and prosencephalon) |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Spinal cord and motor neurons |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Retina |
| Ectoderm | Vertebrate | Posterior pituitary |
See also[]
- Ectoderm
- Endoderm
- Germ layer
- Histogenesis
- Mesoderm
- Eye development
- Heart development
- Limb development
- Germ line development
Notes[]
- ↑ The General category denotes that all or most of the animals containing this layer produce the adjacent product.
- ↑ The Vertebrate category denotes that all or most of the vertebrates containing this layer produce the adjacent product.
References[]
- Evers, Christine A., Lisa Starr. Biology:Concepts and Applications. 6th ed. United States:Thomson, 2006. ISBN 0-534-46224-3.
| Mammalian development of embryo and development and fetus (some dates are approximate - see Carnegie stages) - edit |
|---|
|
Week 1: Zygote | Morula | Blastula/Blastomere/Blastosphere | Archenteron/Primitive streak | Blastopore | Allantois | Trophoblast (Cytotrophoblast | Syncytiotrophoblast | Gestational sac) Week 2: Yolk sac | Vitelline duct | Bilaminar disc Week 3: Hensen's node | Gastrula/Gastrulation | Trilaminar embryo Branchial arch (1st) | Branchial pouch | Meckel's cartilage | Somite/Somitomere | Germ layer (Ectoderm, Endoderm, Mesoderm, Chordamesoderm, Paraxial mesoderm, Intermediate mesoderm, Lateral plate mesoderm) |
| Histogenesis and Organogenesis |
|
Circulatory system: Primitive atrium | Primitive ventricle | Bulbus cordis | Truncus arteriosus | Ostium primum | Foramen ovale | Ductus venosus | Ductus arteriosus | Aortic arches | Septum primum | Septum secundum | Cardinal veins Nervous system: Neural development/Neurulation | Neurula | Neural folds | Neural groove | Neural tube | Neural crest | Neuromere (Rhombomere) | Notochord | Optic vesicles | Optic stalk | Optic cup Digestive system: Foregut | Midgut | Hindgut | Proctodeum | Rathke's pouch | Septum transversum Urinary/Reproductive system: Urogenital folds | Urethral groove | Urogenital sinus | Kidney development (Pronephros | Mesonephros | Ureteric bud | Metanephric blastema) | Fetal genital development (Wolffian duct | Müllerian duct | Gubernaculum | Labioscrotal folds) Glands: Thyroglossal duct Uterine support: Placenta | Umbilical cord (Umbilical artery, Umbilical vein, Wharton's jelly) | Amniotic sac (Amnion, Chorion) |
Germ layers | |
|---|---|
| Germ Layers | |
| Production |
Histogenesis • Organogenesis |
de:Organogenese es:Organogénesis sr:Органогенеза
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |