Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Cognitive Psychology: Attention · Decision making · Learning · Judgement · Memory · Motivation · Perception · Reasoning · Thinking - Cognitive processes Cognition - Outline Index
The sleep stages 1 through 4 are collectively referred to as NREM (non-rapid eye movement) sleep. Rapid eye movement (REM), or stage 5, is not included. There are distinct electroencephalographic characteristics seen in each stage. Unlike REM sleep, there is usually little or no eye movement during this stage. Dreaming is rare during NREM sleep, and the muscles are not paralyzed as in REM sleep. In addition, there is a parasympathetic dominance during NREM.
Stages of NREM sleep[]
NREM sleep is divided into four stages:
- Stage 1 - occurs in the beginning of sleep, with slow eye movements. People in this stage often believe that they are fully awake.
- Stage 2 - the person is unconscious, though awakened easily. No eye movements occur, and dreaming is very rare during this stage. EEG recordings tend to show characteristic "sleep spindles" and "K-complexes" during this stage.
- Stage 3 - transition between stage 2 and stage 4. delta waves begin to occur.
- Stage 4 - slow-wave sleep referred to the "deepest" stage of sleep. Dreaming is more common in this stage than in other stages of NREM sleep though not as common as in REM sleep. The content of SWS dreams tends to be disconnected and not as vivid as those that occur during REM sleep. This is also the most common stage in which parasomnias occur.
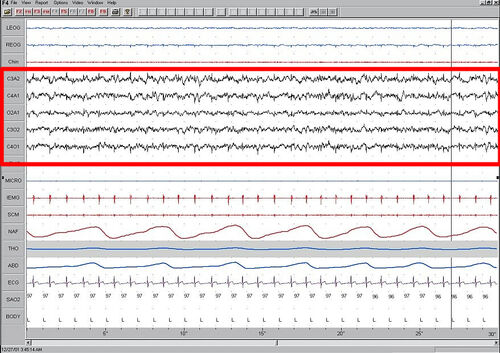
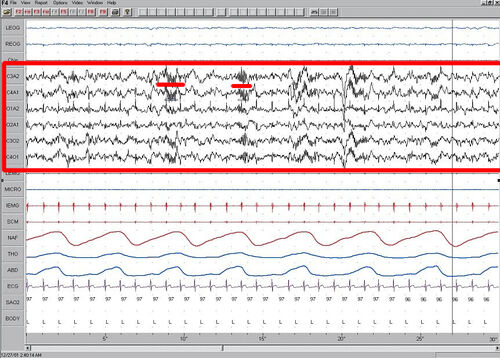
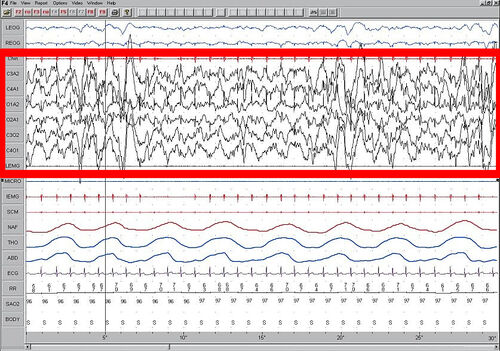
Polysomnography[]
Below are images of each stage of NREM.
The figures represent 30 second epochs (30 seconds of data). They represent data from both eyes, chin, EEG, legs, microphone, intercostal EMG, sterno cloidal mastoid activity, nasal/oral air flow, thoracic effort, abdominal effort, EKG, oxymetry, and body position, in that order. EEG is highlighted by the red box. Sleep spindles in the stage 2 figure are underlined in red.
zh:非REM睡眠
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |