Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
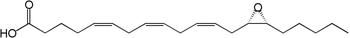
Chemical structure of 14,15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid.
The Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids or EETs are signaling molecules formed by the action of Cytochrome P450 epoxygenase on 20-carbon essential fatty acids, such as arachidonic acid. They act as short-range hormones, (i.e. they are autocrine and paracrine mediators) of the cardiovascular system and kidney. They produce vasorelaxation as well as anti-inflammatory and pro-fibrinolytic effects.[1] Technically they are eicosanoids, though the common use of that term does not yet include them.
Biological effects[]
EETs are cardioprotective after ischemic heart attack and reperfusion.[2] They act in the corpus cavernosumto maintain penile erection.[3]
References[]
- ^ Nithipatikom K, Moore JM, Isbell MA, Falck JR, Gross GJ.. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) in cardioprotection: Ischemic versus reperfusion injury.. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. date=2006 Feb 10. URL accessed on 2006-03-11.
- ^ Jin L, Foss CE, Zhao X, Mills TM, Wang MH, McCluskey LP, Yaddanapud GS, Falck JR, Imig JD, Webb RC.. Cytochrome P450 epoxygenases provide a novel mechanism for penile erection.. FASEB J. 2006 Mar;20(3):539-41.. URL accessed on 2006-03-11.PubMed cite.
- ^ Spector AA,Fang X, Snyder GD, Weintraub NL (Jan 2004). Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs): metabolism and biochemical function. Prog Lipid Res 43 (1): 55-90. PMID 14636671.
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |