Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
| Eardrum | ||
|---|---|---|
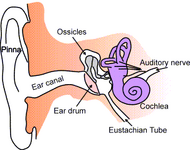
| Anatomy of the human ear. | ||
| Latin | membrana tympani | |
| Gray's | subject #230 1039 | |
| System | ||
| MeSH | A09.246.272.702 | |
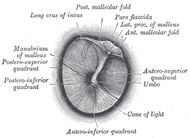
| Right tympanic membrane as seen through a speculum. | ||
The tympanic membrane, colloquially known as the eardrum, is a thin membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit sound from the air to the ossicles inside the middle ear. The malleus bone bridges the gap between the eardrum and the other ossicles.
Rupture or perforation of the eardrum can lead to conductive hearing loss.
Development[]
The tympanic membrane forms from the joining of the expanding first pharyngeal pouch and groove. Around day 30 of gestation, the endoderm-lined first pharyngeal pouch expands to form the tympanic cavity, which subsequently envelops the inner ear ossicles. Simultaneously, the first pharyngeal groove, which is lined with ectoderm, expands to form the developing external auditory meatus. Separated by a thin layer of mesoderm, the tympanic cavity and external auditory meatus join to form the tympanic membrane. As a result, the tympanic membrane is one of very few adult structures that is derived from all three germ layers.
External links[]
Sensory system: Auditory and Vestibular systems (TA A15.3, GA 10.1029) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer ear |
Pinna (Helix, Antihelix, Tragus, Antitragus, Incisura anterior auris, Earlobe) • Ear canal • Auricular muscles Eardrum (Umbo, Pars flaccida) | ||||||||||||||
| Middle ear |
| ||||||||||||||
| Inner ear/ (membranous labyrinth, bony labyrinth) |
| ||||||||||||||
| {| class="navbox collapsible nowraplinks" style="margin:auto; " | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|}
- de:Trommelfell (Anatomie)
es:Tímpano fr:Tympan (anatomie) lt:Būgnelis nl:Trommelvlies pt:Tímpano (ouvido) sr:Бубна опна fi:Tärykalvo
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |