Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
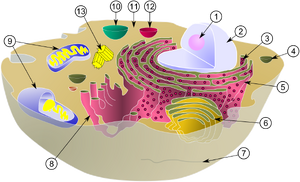
Schematic showing the cytoplasm, with major components of a typical animal cell. Organelles:
(1) nucleolus
(2) nucleus
(3) ribosomes (little dots)
(4) vesicle
(5) rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
(6) Golgi apparatus
(7) Cytoskeleton
(8) smooth ER
(9) mitochondria
(10) vacuole
(11) cytoplasm
(12) lysosome
(13) centrioles within centrosome
The cytoplasm is the parts of a cell that are enclosed within the plasma membrane. In eukaryotic cells the cytoplasm contains organelles, such as mitochondria, that are filled with liquid kept separate from the rest of the cytoplasm by cell membranes. The cytoplasm is the site where most cellular activities occur, such as many metabolic pathways, and processes such as cell division.
The part of the cytoplasm that is not held within organelles is called the cytosol. The cytosol is a complex mixture of cytoskeleton filaments, dissolved molecules, and water that fills much of the volume of a cell. The cytosol is a gel, with a network of fibers dispersed through water. Due to this network of pores and high concentrations of dissolved macromolecules, such as proteins, an effect called macromolecular crowding occurs and the cytosol does not act as an ideal solution. This crowding effect alters how the components of the cytosol interact with each other.
Constituents[]
The cytoplasm has three major elements; the cytosol, organelles and inclusions.
Cytosol[]
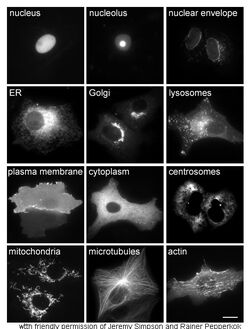
Proteins in different cellular compartments and structures tagged with green fluorescent protein.
The cytosol is the portion of a cell that is not enclosed within membrane-bound organelles. The cytosol is a translucent fluid in which the other cytoplasmic elements are suspended. Cytosol makes up about 70 % of the cell volume and is composed of water, salts and organic molecules.[1] The cytoplasm also contains the protein filaments that make up the cytoskeleton, as well as soluble proteins and large structures such as ribosomes, proteasomes, and the mysterious vault complexes.[2] The inner, granular and more fluid portion of the cytoplasm is referred to as endoplasm.
Organelles[]
Organelles are membrane-bound compartments within the cell that have specific functions. Some major organelles that are suspended in the cytosol are the mitochondria, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and in plant cells chloroplasts.
Cytoplasmic inclusions[]
The inclusions are small particles of insoluble substances suspended in the cytosol. A huge range of inclusions exist in different cell types, and range from crystals of calcium oxalate or silicon dioxide in plants,[3][4] to granules of energy-storage materials such as starchs,[5] glycogen,[6] or polyhydroxybutyrate.[7] A particularly widespread example are lipid droplets, which are spherical droplets composed of lipids and proteins that are used in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes as a way of storing lipids such as fatty acids and sterols.[8] Lipid droplets make up much of the volume of adipocytes, which are specialized lipid-storage cells, but they are also found in a range of other cell types.
References[]
- ↑ Cytoplasm Composition
- ↑ van Zon A, Mossink MH, Scheper RJ, Sonneveld P, Wiemer EA (September 2003). The vault complex. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 60 (9): 1828–37.
- ↑ Prychid, Christina J.; Rudall, Paula J. (1999), "Calcium Oxalate Crystals in Monocotyledons: A Review of their Structure and Systematics", Annals of Botany 84 (6): 725, doi:, http://aob.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/84/6/725
- ↑ Prychid, C. J.; Rudall, P. J.; Gregory, M. (2003), "Systematics and Biology of Silica Bodies in Monocotyledons", The Botanical Review 69 (4): 377–440, doi:, http://www.bioone.org/perlserv/?request=get-abstract
- ↑ Ball SG, Morell MK (2003). From bacterial glycogen to starch: understanding the biogenesis of the plant starch granule. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54: 207–33.
- ↑ Shearer J, Graham TE (April 2002). New perspectives on the storage and organization of muscle glycogen. Can J Appl Physiol 27 (2): 179–203.
- ↑ Anderson AJ, Dawes EA (December 1990). Occurrence, metabolism, metabolic role, and industrial uses of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microbiol. Rev. 54 (4): 450–72.
- ↑ Murphy DJ (September 2001). The biogenesis and functions of lipid bodies in animals, plants and microorganisms. Prog. Lipid Res. 40 (5): 325–438.
Further reading[]
- Alberts, Bruce et al. (2003). Essential Cell Biology, 2nd ed., Garland Science, 2003, ISBN 081533480X.
- Human Anatomy & Physiology, seventh edition By; Elain N Marieb and Latja Hoehn.
External links[]
- What is cytoplasm? - by Genevieve Theirs -2002
- Luby-Phelps K. Cytoarchitecture and physical properties of cytoplasm: volume, viscosity, diffusion, intracellular surface area. Int Rev Cytol. 2000;192:189-221.
| Organelles of the cell |
|---|
| Acrosome | Chloroplast | Cilium/Flagellum | Centriole | Endoplasmic reticulum | Golgi apparatus | Lysosome | Melanosome | Mitochondrion | Myofibril | Nucleus | Parenthesome | Peroxisome | Plastid | Ribosome | Vacuole | Vesicle |
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |